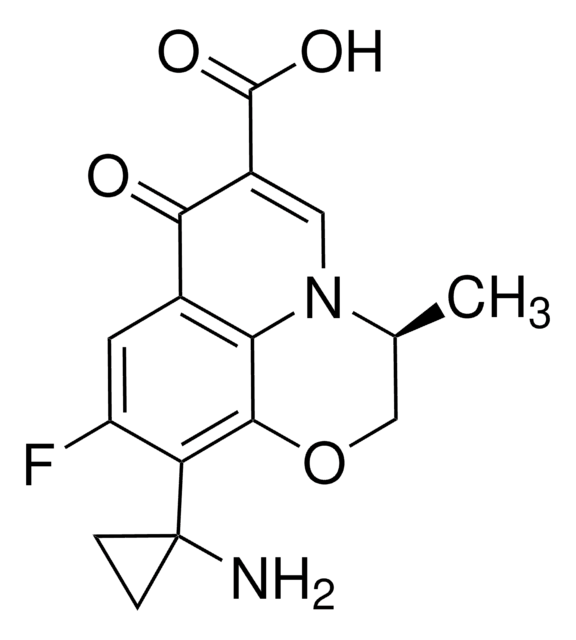
おすすめの製品
由来生物
human carotid artery (normal)
品質水準
包装
pkg of 500,000 cells
メーカー/製品名
Cell Applications, Inc
成長モード
Adherent
核型
2n = 46
形態
Endothelial
テクニック
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
関連疾患
cardiovascular diseases
輸送温度
dry ice
保管温度
−196°C
詳細
Lot specific orders are not able to be placed through the web. Contact your local sales rep for more details.
HCtAEC has been used to elucidate molecular mechanisms of cerebral aneurism caused by haemodynamic (sheer) stress and inflammation, which were shown to act through PGE2-EP2 and NF-κB signaling (Aoki, 2011). Demonstrating a link between inflammation and neovascularization, serum amyloid A, a biomarker of inflammation, increased expression of TNF, F3 factor, NF-κB and VEGF leading to activated migration, wound healing and tube formation responses in HCtAEC; these pro-angiogenic activities could be prevented by pretreatment with the multi-angiokinase receptor inhibitor BIBF1120 (Cai, 2013). Additionally, CD40-CD154 signaling between endothelial cells and T cells leads to a stress response in endothelial cells via activation of NF-κB and MAPK/SAPK pathways and induces down-regulation of APLN, while at the same time activating viral immune surveillance system involving TLR3, IFIH1, RIG-I, and RNASEL (Pluvinet, 2008).
Also, HCtAEC, along with human aortic (HAOEC), brachiocephalic artery (HBcAEC), coronary artery (HCAEC) and subclavian artery (HScAEC) have been used to demonstrate that not only blood vessels from different tissues are highly heterogeneous, they also interact differently with leukocytes during the inflammation response (Scott, 2013). The authors further showed that differential N-glycosylation of commonly expressed vascular adhesion molecules may be responsible for this heterogeneity, as well as for modulation of signaling under resting and activated inflammatory conditions. This also explains why specific vascular beds may be more or less susceptible to particular diseases or stimuli. Importantly, if cells from different sources were used, these results could not be convincingly validated due to a number of uncontrolled variables, such as age, race, genetic variability or life style choices of the donors.
Because of the complex heterogeneity that exists not only between different donors, but even between different vascular beds in the same individual, it would be prudent to confirm any new findings on primary cell lots coming from several different origins.
HCtAEC has been used to elucidate molecular mechanisms of cerebral aneurism caused by haemodynamic (sheer) stress and inflammation, which were shown to act through PGE2-EP2 and NF-κB signaling (Aoki, 2011). Demonstrating a link between inflammation and neovascularization, serum amyloid A, a biomarker of inflammation, increased expression of TNF, F3 factor, NF-κB and VEGF leading to activated migration, wound healing and tube formation responses in HCtAEC; these pro-angiogenic activities could be prevented by pretreatment with the multi-angiokinase receptor inhibitor BIBF1120 (Cai, 2013). Additionally, CD40-CD154 signaling between endothelial cells and T cells leads to a stress response in endothelial cells via activation of NF-κB and MAPK/SAPK pathways and induces down-regulation of APLN, while at the same time activating viral immune surveillance system involving TLR3, IFIH1, RIG-I, and RNASEL (Pluvinet, 2008).
Also, HCtAEC, along with human aortic (HAOEC), brachiocephalic artery (HBcAEC), coronary artery (HCAEC) and subclavian artery (HScAEC) have been used to demonstrate that not only blood vessels from different tissues are highly heterogeneous, they also interact differently with leukocytes during the inflammation response (Scott, 2013). The authors further showed that differential N-glycosylation of commonly expressed vascular adhesion molecules may be responsible for this heterogeneity, as well as for modulation of signaling under resting and activated inflammatory conditions. This also explains why specific vascular beds may be more or less susceptible to particular diseases or stimuli. Importantly, if cells from different sources were used, these results could not be convincingly validated due to a number of uncontrolled variables, such as age, race, genetic variability or life style choices of the donors.
Because of the complex heterogeneity that exists not only between different donors, but even between different vascular beds in the same individual, it would be prudent to confirm any new findings on primary cell lots coming from several different origins.
細胞株の由来
Artery
アプリケーション
neovascularization, cell migration, wound healing, tube formation, angiogenesis, signal tranduction, monocyte chemotactic factor production, cell adhesion
構成
Basal Medium containing 10% FBS & 10% DMSO
調製ノート
- 2nd passage, >500,000 cells in Basal Medium containing 10% FBS & 10% DMSO
- Can be cultured at least 10 doublings
継代と培養方法
Please refer to the HCtAEC Culture Protocol.
免責事項
RESEARCH USE ONLY. This product is regulated in France when intended to be used for scientific purposes, including for import and export activities (Article L 1211-1 paragraph 2 of the Public Health Code). The purchaser (i.e. enduser) is required to obtain an import authorization from the France Ministry of Research referred in the Article L1245-5-1 II. of Public Health Code. By ordering this product, you are confirming that you have obtained the proper import authorization.
保管分類コード
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
3014-05A:
最新バージョンのいずれかを選択してください:
プロトコル
Technical information for working with human carotid artery endothelial cells including thawing, subculturing and cryopreservation
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)

![イミダゾ[1,2-a]ピリジン 99%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/109/863/81ccb63f-07c6-4271-b317-1ba58979d455/640/81ccb63f-07c6-4271-b317-1ba58979d455.png)