おすすめの製品
グレード
for molecular biology
品質水準
形状
liquid (aqueous solution)
使用法
mL (suitable for 165 transfections)
包装
pkg of 0.4 mL (06365779001)
pkg of 1.0 mL (06365787001)
pkg of 5 × 1.0 mL (06365809001)
メーカー/製品名
Roche
テクニック
transfection: suitable
保管温度
2-8°C
関連するカテゴリー
詳細
アプリケーション
X-tremeGENE™ 9 DNAトランスフェクション試薬は、以下のような細胞の分析用途に適しています:
- 機能解析のための組換えタンパク質の発現。
- 代謝経路の生理学的研究。
- レポーター遺伝子アッセイを用いた調節配列の分析。
- 遺伝子発現アッセイ。
- がん研究試験。
- 標的評価。
特徴および利点
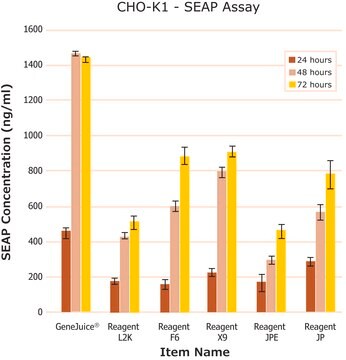
- トランスフェクション後の細胞生存率を最大限にするため、細胞毒性が極めて低い試薬を用いて生理学的に適切な結果を生み出してください。
- X-tremeGENE 9 DNAトランスフェクション試薬を単に希釈し、プラスミドDNAとともにインキュベートし、混合液を細胞に直接ピペットで加えます(血清ありまたは血清なし)。
- 一般的に使用される細胞株では時間のかかる最適化手順を避けてください。
品質
物理的形状
その他情報
法的情報
関連製品
シグナルワード
Danger
危険有害性情報
危険有害性の分類
Eye Irrit. 2 - Flam. Liq. 2
保管分類コード
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 1
引火点(°F)
334.4 °F
引火点(℃)
168 °C
試験成績書(COA)
製品のロット番号・バッチ番号を入力して、試験成績書(COA) を検索できます。ロット番号・バッチ番号は、製品ラベルに「Lot」または「Batch」に続いて記載されています。
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
資料
Automation is used for many applications to reduce variation caused by manual handling and to obtain reproducible results in high-throughput assays. High-throughput applications, such as knockdown studies or target screenings, often include cell transfection.
Automation is used for many applications to reduce variation caused by manual handling and to obtain reproducible results in high-throughput assays. High-throughput applications, such as knockdown studies or target screenings, often include cell transfection.
Small inhibitory RNAs (siRNAs) have become the focus of interest in many laboratories. For the first time, these molecules offer an easy way to knock down the expression of selected genes in mammalian cells without having to resort to classical gene knockout techniques.
Small inhibitory RNAs (siRNAs) have become the focus of interest in many laboratories. For the first time, these molecules offer an easy way to knock down the expression of selected genes in mammalian cells without having to resort to classical gene knockout techniques.
プロトコル
Plate cells approx. 24 hours before transfection making sure cells are at optimal concentration (70 – 90 % confluency).
Cell preparation for transfection Plate cells approx. 24 hours before transfection making sure cells are at optimal concentration (70 – 90 % confluency).
Transient co-transfection of plasmids is a method that is commonly employed for cellular protein-protein interaction studies, transcription factor studies, and gene knockdown studies using shRNA encoding plasmids.
Protocols for Transfecting Common Cell Lines with X-tremeGENE™ Transfection Reagents
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)