おすすめの製品
由来生物
rabbit
品質水準
抗体製品の状態
serum
抗体製品タイプ
primary antibodies
クローン
polyclonal
フォーム
liquid
含まれません
preservative
交差性
mouse, human, rat
メーカー/製品名
Calbiochem®
保管条件
OK to freeze
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
アイソタイプ
IgG
輸送温度
wet ice
保管温度
−70°C
ターゲットの翻訳後修飾
unmodified
詳細
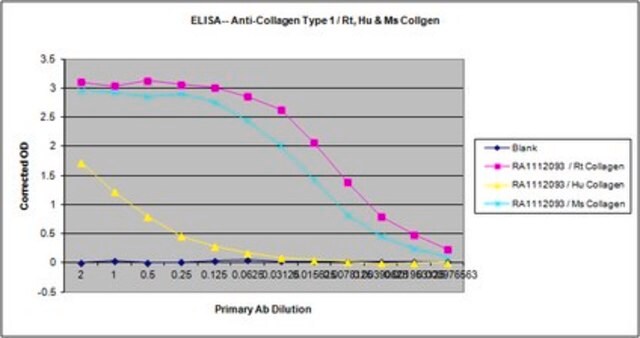
Rabbit polyclonal antibody supplied as undiluted serum. Recognizes the ~115 kDa (doublet) type I collagen protein.
Recognizes type I collagen. Exhibits slight cross-reactivity with type III collagen.
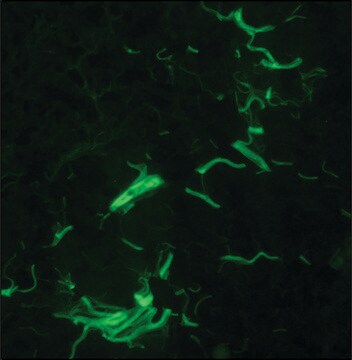
This Anti-Collagen Type I Rabbit pAb is validated for use in Frozen Sections, Immunoblotting, Immunofluorescence, Immunoprecipitation for the detection of Collagen Type I.
免疫原
Fetal Mouse Skin
purified, fetal mouse skin collagen type I
アプリケーション
Frozen Sections (1:30-1:60, see comments)
Immunoblotting (1:200-1:500)
Immunofluorescence (1:20-1:40)
Immunoprecipitation (1:20-1:60)
Immunoblotting (1:200-1:500)
Immunofluorescence (1:20-1:40)
Immunoprecipitation (1:20-1:60)
警告
Toxicity: Standard Handling (A)
物理的形状
Undiluted serum.
再構成
Following initial thaw, aliquot and freeze (-70°C).
その他情報
Romanos, G.E., et al. 1992. J. Periodont. Res. 27, 101.
Zimmermann, B., et al. 1992. Eur. Arch. Biol. 103, 93.
Schröter-Kermani, C., et al. 1991. Matrix 11, 428.
Zimmermann, B., et al. 1992. Eur. Arch. Biol. 103, 93.
Schröter-Kermani, C., et al. 1991. Matrix 11, 428.
法的情報
CALBIOCHEM is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
適切な製品が見つかりませんか。
製品選択ツール.をお試しください
保管分類コード
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
234167-500UL:
234167-UL:
試験成績書(COA)
製品のロット番号・バッチ番号を入力して、試験成績書(COA) を検索できます。ロット番号・バッチ番号は、製品ラベルに「Lot」または「Batch」に続いて記載されています。
Dingqi Zhang et al.
Pharmaceutical biology, 58(1), 1229-1243 (2020-12-18)
Xiayuxue decoction (XYXD), a traditional Chinese medicine, is used for treating liver disease. However, the potential active constituents and mechanisms are still unclear. To explore the main active fraction extracts, active ingredients and possible mechanisms of XYXD for anti-hepatic fibrosis.
Michel Fausther et al.
Purinergic signalling, 13(4), 417-428 (2017-07-02)
Hepatic fibrosis represents a pathological wound healing and tissue repair process triggered in response to chronic liver injury. A heterogeneous population of activated non-parenchymal liver cells, known as liver myofibroblasts, functions as the effector cells in hepatic fibrosis. Upon activation
Patricia Gallego-Muñoz et al.
Journal of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, 12(2), e737-e746 (2016-11-20)
The development of treatments that modulate corneal wound healing to avoid fibrosis during tissue repair is important for the restoration of corneal transparency after an injury. To date, few studies have studied the influence of growth factors (GFs) on human
Kristin V T Engebretsen et al.
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985), 114(8), 988-997 (2013-02-16)
On the basis of the role of small, leucine-rich proteoglycans (SLRPs) in fibrogenesis and inflammation, we hypothesized that they could be involved in cardiac remodeling and reverse remodeling as occurs during aortic stenosis and after aortic valve replacement. Thus, in
Cédric P Laurent et al.
Journal of biomaterials applications, 32(9), 1276-1288 (2018-02-08)
Poly(lactide-co-ε-caprolactone) (PLCL) has been reported to be a good candidate for tissue engineering because of its good biocompatibility. Particularly, a braided PLCL scaffold (PLL/PCL ratio = 85/15) has been recently designed and partially validated for ligament tissue engineering. In the present study
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)