F0427
Fas Ligand human
>95% (SDS-PAGE), recombinant, expressed in CHO cells, lyophilized powder
Sinonimo/i:
FasL
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Ricombinante
expressed in CHO cells
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
>95% (SDS-PAGE)
Stato
lyophilized powder
PM
monomer calculated mol wt ~18 kDa
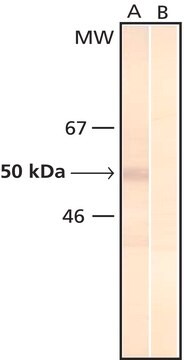
26-28 kDa by SDS-PAGE
Impurezze
endotoxin, tested
N° accesso UniProt
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Informazioni sul gene
human ... FASLG(356)
Categorie correlate
Descrizione generale
FASLG (Fas ligand) acts as a ligand for Fas receptor, and is a major protein involved in programmed cell death, apoptosis. Soluble Fas (sFAS) is usually detected in plasma prior to apoptosis.
Applicazioni
Fas Ligand (FASLG) human has been used for-
- the study of FASLG stimulation in luteal cells obtained from mid-corpus luteum (CL) and
- the study of apoptosis induction and intracellular caspase-3 assay in human cells.
Azioni biochim/fisiol
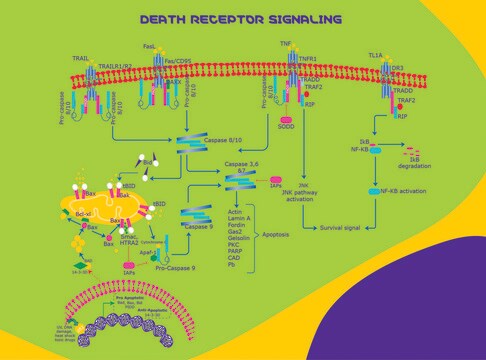
FASLG (Fas ligand) and Fas receptor constitute the basic elements in apoptosis. Interaction of FASLG with Fas receptor leads to activation of caspase-8. This caspase in turn leads to activation of effector caspases such as caspase-3, -6 and -7. This cascade results in the hydrolysis of nuclear and cytoplasmic components. Expression of FASLG is induced by nuclear factor-κB (NFκB). NFκB/FASLG pathway facilitates the suppression of p,p′-DDT (dichlorodiphenoxytrichloroethane)-induced cell toxicity by vitamin C and E. In CD4+ T cells, this protein is expressed on stimulus by T-cell receptor (TCR), both during normal and pathological conditions, such as alcohol exposure.
Fas ligand, a protein belonging to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family of cytokines, induces apoptosis in cells expressing the cell membrane receptor Fas (CD95/Apo-1).
Protein belonging to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family of cytokines; induces apoptosis in cells expressing the cell membrane receptor Fas (CD95/Apo-1).
Altre note
Human Fas Ligand, N-terminal 6X histidine-tagged, encodes amino acids 134-281.
Stato fisico
Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in phosphate buffered saline containing 0.5 mg bovine serum albumin.
Risultati analitici
Measured by its ability to induce apoptosis in Jurkat cells.
Avvertenze
Warning
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Malavika S Giri et al.
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950), 182(7), 4459-4470 (2009-03-21)
Mechanisms that may allow circulating monocytes to persist as CD4 T cells diminish in HIV-1 infection have not been investigated. We have characterized steady-state gene expression signatures in circulating monocytes from HIV-infected subjects and have identified a stable antiapoptosis gene
Xiaoting Jin et al.
PloS one, 9(12), e113257-e113257 (2014-12-03)
Dichlorodiphenoxytrichloroethane (DDT) is a known persistent organic pollutant and liver damage toxicant. However, there has been little emphasis on the mechanism underlying liver damage toxicity of DDT and the relevant effective inhibitors. Hence, the present study was conducted to explore
Aleksander Szymanowski et al.
Atherosclerosis, 233(2), 616-622 (2014-02-19)
Apoptosis of natural killer (NK) cells is increased in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) and may explain why NK cell levels are altered in these patients. Soluble forms of Fas and Fas ligand (L) are considered as markers of
Antonio M Galvao et al.
Biology of reproduction, 83(6), 901-908 (2010-08-20)
Proapoptotic factor Fas ligand (FASL) and its cell surface receptor FAS are tumor necrosis factor superfamily members that trigger apoptosis in different cell types. However, their influence on luteal steroidogenesis is not clearly understood. The aim of the present work
Intracellular bacteria engage a STING-TBK1-MVB12b pathway to enable paracrine cGAS-STING signalling.
Ramya Nandakumar et al.
Nature microbiology, 4(4), 701-713 (2019-02-26)
The innate immune system is crucial for eventual control of infections, but may also contribute to pathology. Listeria monocytogenes is an intracellular Gram-positive bacteria and a major cause of food-borne disease. However, important knowledge on the interactions between L. monocytogenes
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.