F0552
Fas Ligand from mouse
>95% (SDS-PAGE), recombinant, expressed in mouse NSO cells, lyophilized powder
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Ricombinante
expressed in mouse NSO cells
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
>95% (SDS-PAGE)
Stato
lyophilized powder
PM
monomer calculated mol wt ~18 kDa
28-32 kDa by SDS-PAGE
Impurezze
endotoxin, tested
N° accesso UniProt
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Informazioni sul gene
mouse ... Fasl(14103)
Descrizione generale
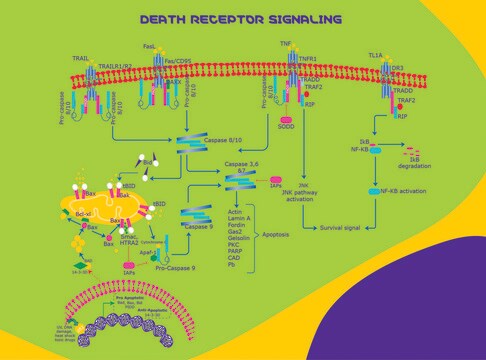
FASLG (Fas ligand) acts as a ligand for Fas receptor, and is a major protein involved in programmed cell death, apoptosis. Soluble Fas (sFAS) is usually detected in plasma prior to apoptosis.
Applicazioni
Fas Ligand (FASLG) from mouse has been used for-
- the induction of apoptosis in PC12 cells and
- the induction of migration in BV-2 murine microglial cells.
Azioni biochim/fisiol
FASLG (Fas ligand) and Fas receptor constitute the basic elements in apoptosis. Interaction of FASLG with Fas receptor leads to activation of caspase-8. This caspase in turn leads to activation of effector caspases such as caspase-3, -6 and -7. This cascade results in the hydrolysis of nuclear and cytoplasmic components. Expression of FASLG is induced by nuclear factor-κB (NFκB). NFκB/FASLG pathway facilitates the suppression of p,p′-DDT (dichlorodiphenoxytrichloroethane)-induced cell toxicity by vitamin C and E. In CD4+ T cells, this protein is expressed on stimulus by T-cell receptor (TCR), both during normal and pathological conditions, such as alcohol exposure.
Fas ligand, a protein belonging to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family of cytokines, induces apoptosis in cells expressing the cell membrane receptor Fas (CD95/Apo-1).
Protein belonging to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family of cytokines; induces apoptosis in cells expressing the cell membrane receptor Fas (CD95/Apo-1).
Altre note
Mouse Fas Ligand, N-terminal 6X histidine-tagged, encodes amino acid residues 132-279.
Stato fisico
Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in phosphate buffered saline containing 2.5 mg bovine serum albumin.
Risultati analitici
Measured by its ability to induce apoptosis in Jurkat cells.
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Xiaoting Jin et al.
PloS one, 9(12), e113257-e113257 (2014-12-03)
Dichlorodiphenoxytrichloroethane (DDT) is a known persistent organic pollutant and liver damage toxicant. However, there has been little emphasis on the mechanism underlying liver damage toxicity of DDT and the relevant effective inhibitors. Hence, the present study was conducted to explore
Aleksander Szymanowski et al.
Atherosclerosis, 233(2), 616-622 (2014-02-19)
Apoptosis of natural killer (NK) cells is increased in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) and may explain why NK cell levels are altered in these patients. Soluble forms of Fas and Fas ligand (L) are considered as markers of
Nicole Suyun Liu et al.
PloS one, 7(8), e43180-e43180 (2012-08-21)
Diva is a member of the Bcl2 family but its function in apoptosis remains largely unclear because of its specific expression found within limited adult tissues. Previous overexpression studies done on various cell lines yielded conflicting conclusions pertaining to its
Ying-mei Lu et al.
Journal of neuroinflammation, 9, 172-172 (2012-07-14)
The cerebral microvascular occlusion elicits microvascular injury which mimics the different degrees of stroke severity observed in patients, but the mechanisms underlying these embolic injuries are far from understood. The Fas ligand (FasL)-Fas system has been implicated in a number
Smita S Ghare et al.
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950), 193(1), 412-421 (2014-06-06)
Activation-induced Fas ligand (FasL) mRNA expression in CD4+ T cells is mainly controlled at transcriptional initiation. To elucidate the epigenetic mechanisms regulating physiologic and pathologic FasL transcription, TCR stimulation-responsive promoter histone modifications in normal and alcohol-exposed primary human CD4+ T
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.