推荐产品
應用
人肾细胞产生的尿激酶已被用作消化混合物的成分,用于三维纤维蛋白培养。也用于纤溶酶原激活试验。
生化/生理作用
尿激酶可促进肾肿瘤细胞的增殖。
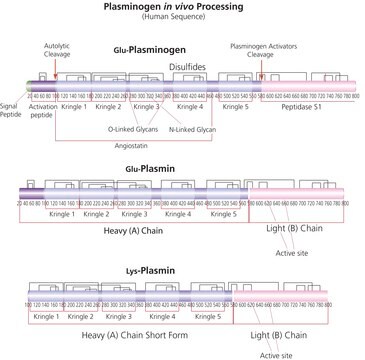
尿激酶是一种蛋白酶,能裂解纤溶酶原形成纤溶酶。与细胞表面受体 (uPAR) 结合,在组织重塑过程中调节细胞粘附和迁移,并激活细胞内信号通路。尿激酶由三个结构域组成:与表皮生长因子同源的氨基末端结构域通过中央圈形区结构域连接到羧基端的蛋白酶结构域。
物理性質
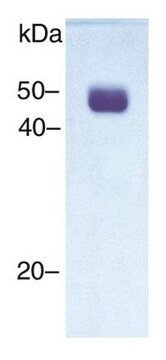
主要活性成分是尿激酶的低分子量形式,由 2,000 道尔顿的 A 链和 30,400 道尔顿的 B 链通过巯基键连接而成。
供应的冻干粉,含有人血白蛋白、甘露醇和 NaCl。
其他說明
注:当人纤维蛋白溶酶原作为底物时,活性更高。
訊號詞
Danger
危險聲明
危險分類
Resp. Sens. 1
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
其他客户在看
The multifaceted roles of Leptospira enolase
Salazar N, et al.
Research in Microbiology, 168(2), 157-164 (2017)
J C Kirchheimer et al.
Carcinogenesis, 9(11), 2121-2123 (1988-11-01)
Primary cultures of renal cell carcinomas and of the corresponding normal adjacent kidney tissue from 6 patients were analyzed for the effects of exogenously added urokinase-type plasminogen activator on cell proliferation as compared to the effects of tissue type plasminogen
Hematopoietic-to-mesenchymal transition of adipose tissue macrophages is regulated by integrin beta and fabricated fibrin matrices
Gavin KM, et al.
Adipocyte, 6(3), 234-249 (2017)
H R Lijnen et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 265(9), 5232-5236 (1990-03-25)
The mechanism of the activation of plasminogen by single-chain urokinase-type plasminogen activator (single-chain u-PA, scu-PA) was studied using rscu-PA-Glu158, a recombinant plasmin-resistant mutant of human scu-PA obtained by site-specific mutagenesis of Lys158 to Glu, and rPlg-Ala740, a recombinant human plasminogen
Helena Enocsson et al.
Translational research : the journal of laboratory and clinical medicine, 162(5), 287-296 (2013-08-07)
Assessments of disease activity and organ damage in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) remain challenging because of the lack of reliable biomarkers and disease heterogeneity. Ongoing inflammation can be difficult to distinguish from permanent organ damage caused by previous flare-ups or
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门