推荐产品
用途
(Fluorometric MDR Assay)
應用
pharmaceutical
檢測方法
fluorometric
相關疾病
cancer
儲存溫度
−20°C
基因資訊
human ... ABCB1(5243) , ABCC2(1244)
mouse ... ABCC2(12780)
rat ... abcc2(25303)
一般說明
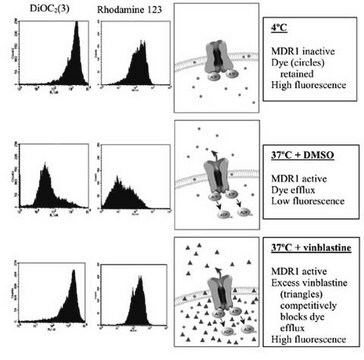
Acquired resistance to chemotherapy drugs, multidrug resistance or MDR, is a major contributor to treatment failure for many types of cancers. MDR is typically associated with the increased expression of two ATP-dependent drug efflux pumps, P-Glycoprotein (P-gp or MDR1) and the Multidrug Resistance-Associated Protein (MRP1). These pumps actively expel chemotherapeutic agents, typically hydrophobic amphipathic natural products, from the cytoplasm to exterior of the cell.
This kit is utilizes a hydrophobic fluorescent dye molecule to assess MDR activity in cells. This dye rapidly penetrates cell membranes and becomes trapped resulting in an increase in fluorescence intensity (λex = 490/λem = 525 nm). In cells expressing MDR transporters, the dye is rapidly extruded by the transporters, resulting in decreased fluorescence intensity.
This kit is utilizes a hydrophobic fluorescent dye molecule to assess MDR activity in cells. This dye rapidly penetrates cell membranes and becomes trapped resulting in an increase in fluorescence intensity (λex = 490/λem = 525 nm). In cells expressing MDR transporters, the dye is rapidly extruded by the transporters, resulting in decreased fluorescence intensity.
特點和優勢
Compatible with high-throughput handling systems.
適合性
This kit is suitable for the screening of MDR pump inhibitors or for identifying cell lines with high MDR activity.
原則
This kit is utilizes a hydrophobic fluorescent dye molecule to assess MDR activity in cells. This dye rapidly penetrates cell membranes and becomes trapped resulting in an increase in fluorescence intensity (λEx = 490/λEm = 525 nm). In cells expressing MDR transporters, the dye is rapidly extruded by the transporters, resulting in decreased fluorescence intensity.
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
Drug resistance in cancer: an overview.
Housman G, et al.
Cancer, 6(3), 1769-1792 (2014)
Non-coding polymorphisms in nucleotide binding domain 1 in ABCC1 gene associate with transcript level and survival of patients with breast cancer.
Kunicka T, et al.
PLoS ONE, 9(7), e101740-e101740 (2014)
Mechanisms and insights into drug resistance in cancer.
Zahreddine H and Katherine B
Frontiers in Pharmacology, 4, 28-28 (2013)
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门