推荐产品
描述
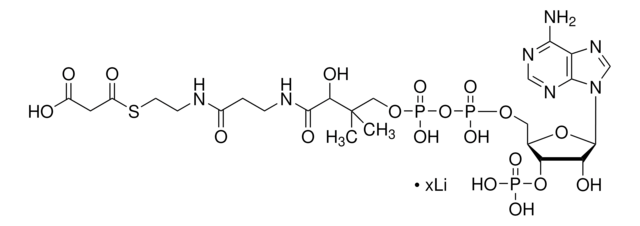
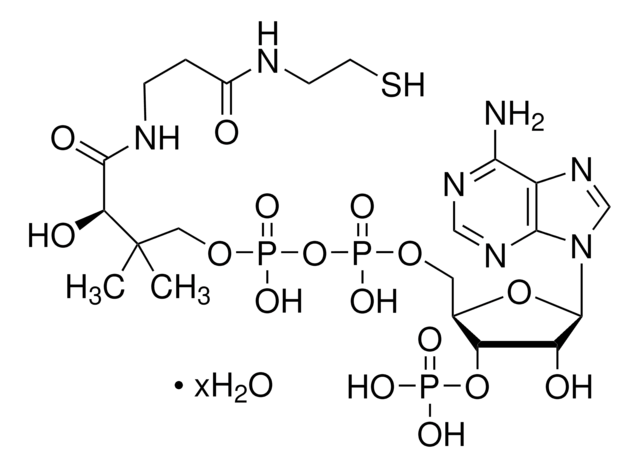
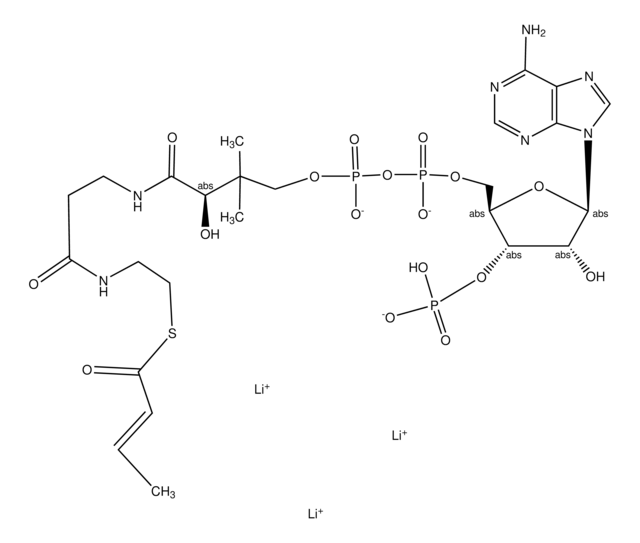
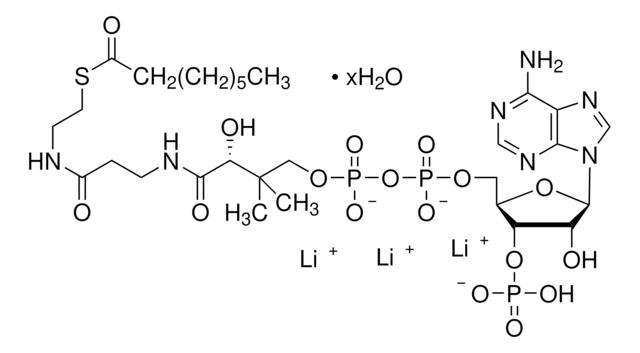
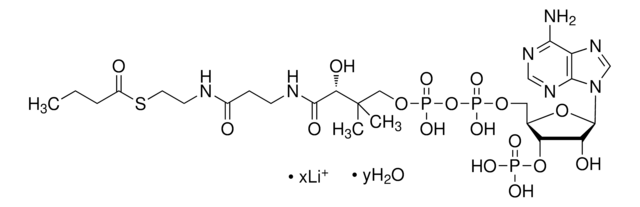
Chemical Formula: C23H35N7O17P3SLi3
品質等級
化驗
85% (Enzymatic and Absorbance)
形狀
solid
分子量
Mr 809.6 (acetyl-CoA)
Mr 827.4 (acetyl-CoA-Li3)
包裝
pkg of 010 mg (10101893001)
pkg of 200 mg (11585371001)
pkg of 050 mg (10101907001)
製造商/商標名
Roche
濃度
2% (lithium)
儲存溫度
2-8°C
一般說明
乙酰辅酶 A,三锂盐
應用
乙酰辅酶 A 用于使用放射性同位素测定细胞提取物中的 CAT 酶活性。细胞提取物中的 CAT 酶活性催化乙酰基从乙酰辅酶 A 转移到氯霉素。已经开发了许多测定来测量细胞提取物中的 CAT 活性。乙酰辅酶 A 也已用于测定柠檬酸合酶活性。
生化/生理作用
乙酰辅酶 A(Ac-CoA)是糖酵解的最终产物,参与 Ac-CoA 途径,这是碳化合物的代谢途径。Ac-CoA 在胆固醇合成中十分重要。它还参与脂肪酸的生物合成和多胺(如精胺和亚精胺)的分解代谢。低水平的 Ac-CoA 导致神经胶质细胞和神经元功能的丧失。酮体和甘油三酯在水解时产生 Ac-CoA,这间接导致组蛋白乙酰化增加。
準備報告
工作溶液:最佳溶剂:具有弱酸性 pH(4 至 5)的水或水溶液。
储存条件(工作溶液):-15 至 -25°C
50mg/ml 磷酸盐缓冲液,pH 7,在 -15 至 -25℃ 下,可稳定保存 3 周。未冻存的溶液应立即使用。
储存条件(工作溶液):-15 至 -25°C
50mg/ml 磷酸盐缓冲液,pH 7,在 -15 至 -25℃ 下,可稳定保存 3 周。未冻存的溶液应立即使用。
其他說明
仅用于生命科学研究。不可用于诊断。
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
其他客户在看
L Lu et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 271(31), 18920-18924 (1996-08-02)
Polyamine catabolism is rate limited by spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase (SSAT). Although the amino acid sequence of SSAT is known, the substrate binding and catalytic sites are not. The goal of this study was to define the region responsible for acetyl coenzyme
Biochemistry null
Eileen B Ekstrom et al.
Applied and environmental microbiology, 69(9), 5414-5422 (2003-09-06)
Sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) in anoxic waters and sediments are the major producers of methylmercury in aquatic systems. Although a considerable amount of work has addressed the environmental factors that control methylmercury formation and the conditions that control bioavailability of inorganic
Short-term variation of nutritive and metabolic parameters in Temora longicornis females (Crustacea, Copepoda) as a response to diet shift and starvation
Tobias Kreibich
Helgoland Marine Research , 62(3), 241-249 (2008)
Agnieszka Jankowska-Kulawy et al.
Neurochemistry international, 57(7), 851-856 (2010-09-21)
Several pathologic conditions are known to cause thiamine deficiency, which induce energy shortages in all tissues, due to impairment of pyruvate decarboxylation. Brain is particularly susceptible to these conditions due to its high rate of glucose to pyruvate-driven energy metabolism.
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门