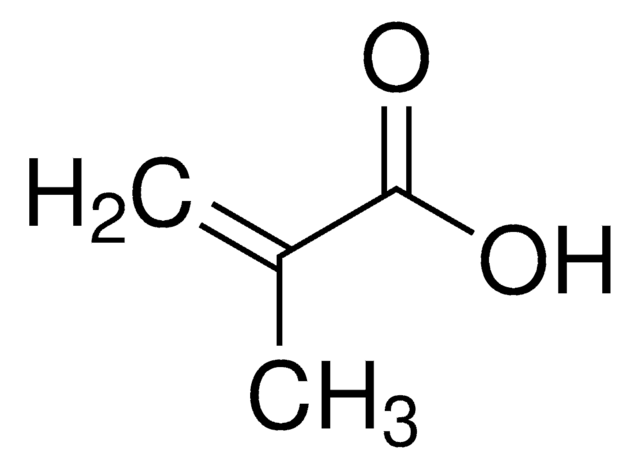
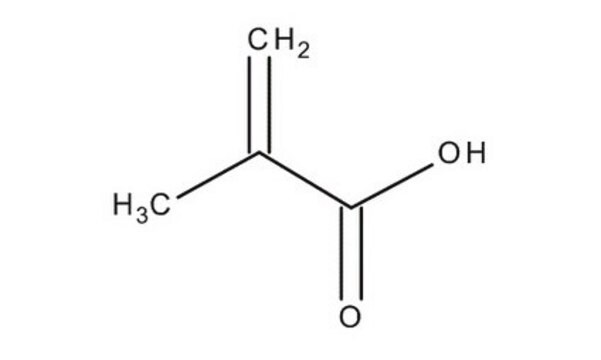
推荐产品
品質等級
化驗
≥94%
形狀
liquid
包含
2,000 ppm topanol A as inhibitor
折射率
n20/D 1.453 (lit.)
bp
87 °C/13 mmHg (lit.)
密度
1.035 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES 字串
CC(=C)C(=O)OC(=O)C(C)=C
InChI
1S/C8H10O3/c1-5(2)7(9)11-8(10)6(3)4/h1,3H2,2,4H3
InChI 密鑰
DCUFMVPCXCSVNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
正在寻找类似产品? 访问 产品对比指南
一般說明
甲基丙烯酸酐是一种有机化合物,来源于甲基丙烯酸,属于丙烯酸类。它主要用作聚合物的单体,特别是聚(甲基丙烯酸)及其共聚物的生产中。由于其优异的化学和热稳定性,这些聚合物在广泛的行业中应用,包括生物可再生树脂、pH敏感水凝胶、热固性树脂、涂料、胶粘剂和塑料。在甲基丙烯酸酐的聚合过程中,最常用的抑制剂是Topanol A。通常以小量(2000 ppm)添加,以阻止在聚合过程中不良的副反应,确保受控和高质量的聚合物形成。
應用
甲基丙烯酸酐可用作合成以下材料的起始物:
- 通过共聚反应合成甲基丙烯酰化软骨素硫酸盐pH敏感水凝胶。这些水凝胶可用于药物传递系统。
- 高性能木质素基热固性树脂。
- 凝胶聚合物电解质,然后与阴极集成以形成高性能锂离子电池。
訊號詞
Danger
危險分類
Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT SE 3
標靶器官
Respiratory system
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 2
閃點(°F)
183.2 °F - closed cup
閃點(°C)
84 °C - closed cup
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
其他客户在看
Notes-Acrylic and Methacrylic Anhydrides.
Brotherton T, et al.
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 26(4), 1283-1284 (1961)
A I Van Den Bulcke et al.
Biomacromolecules, 1(1), 31-38 (2001-11-17)
Dynamic shear oscillation measurements at small strain were used to characterize the viscoelastic properties and related differences in the molecular structure of hydrogels based on gelatin methacrylamide. Gelatin was derivatized with methacrylamide side groups and was subsequently cross-linked by radical
G Bahcecioglu et al.
Biomaterials, 218, 119361-119361 (2019-07-25)
A PCL/hydrogel construct that would mimic the structural organization, biochemistry and anatomy of meniscus was engineered. The compressive (380 ± 40 kPa) and tensile modulus (18.2 ± 0.9 MPa) of the PCL scaffolds were increased significantly when constructs were printed with a shifted design and circumferential
Efficient catechol functionalization of biopolymeric hydrogels for effective multiscale bioadhesion.
Kunyu Zhang et al.
Materials science & engineering. C, Materials for biological applications, 103, 109835-109835 (2019-07-28)
Hydrogels are promising soft materials for the delivery of therapeutic cells and cargo molecules. Inspired by mussel adhesion chemistry, hydrogels based on catechol (Cat)-modified polysaccharides have been developed to enhance hydrogel-tissue interactions. However, due to the inevitable side reactions such
Avathamsa Athirasala et al.
Scientific reports, 7(1), 3323-3323 (2017-06-14)
The requirement for immediate vascularization of engineered dental pulp poses a major hurdle towards successful implementation of pulp regeneration as an effective therapeutic strategy for root canal therapy, especially in adult teeth. Here, we demonstrate a novel strategy to engineer
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门