C9301
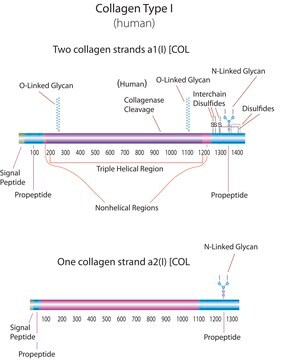
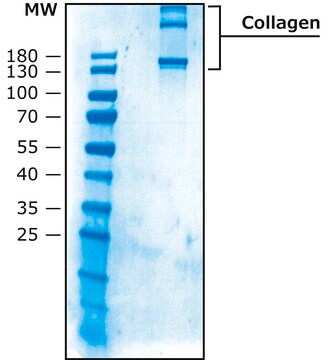
Chicken Collagen Type II
from chicken sternal cartilage, powder, suitable for cell culture
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
product name
Collagen from chicken sternal cartilage, Type II (Miller), powder, BioReagent, suitable for cell culture
Origine biologica
chicken (Sternal cartilage)
Livello qualitativo
Tipo
Type II (Miller)
Nome Commerciale
BioReagent
Forma fisica
powder
Confezionamento
glass bottle of 100 mg
poly bottle of 25 mg
glass bottle of 5 mg
Concentrazione
60-80% (biuret)
tecniche
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
Copertura della superficie
6‑10 μg/cm2
Solubilità
acetic acid: 0.5-2.0 mg/mL (Dissolve for several hours at 2-8 °C, occasionally swirling.)
N° accesso UniProt
Specificità del legame
Peptide Source: Fibrinogen
Condizioni di spedizione
wet ice
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
Informazioni sul gene
chicken ... COL2A1(395069)
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
- in enzyme–linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
- chondrocyte-mediated tissue production in vitro.
- induction, treatment, and assessment of collagenα induced arthritis (CIA).
- cell proliferation assay.
- as a coating for cell culture surfaces.
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Caratteristiche e vantaggi
Altre note
Nota sulla preparazione
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Articoli
Cancer stem cell media, spheroid plates and cancer stem cell markers to culture and characterize CSC populations.
Extracellular matrix proteins such as laminin, collagen, and fibronectin can be used as cell attachment substrates in cell culture.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.