T7394
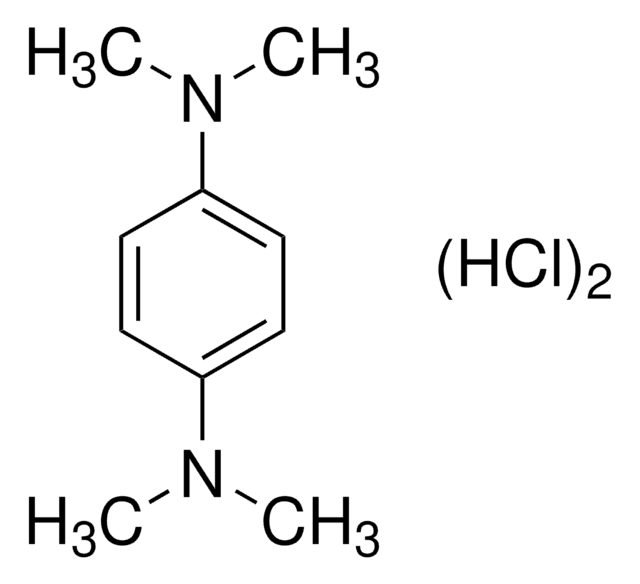
N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine
99%, powder
Sinonimo/i:
TMPD, TMPDA, TMPPD, Wurster’s reagent
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Formula condensata:
C6H4[N(CH3)2]2
Peso molecolare:
164.25
Beilstein:
1564025
Numero CE:
Numero MDL:
Codice UNSPSC:
12352100
ID PubChem:
NACRES:
NA.22
Prodotti consigliati
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
99%
Stato
flakes
powder
Colore
off-white to brown
P. ebollizione
260 °C (lit.)
Punto di fusione
49-51 °C (lit.)
Stringa SMILE
CN(C)c1ccc(cc1)N(C)C
InChI
1S/C10H16N2/c1-11(2)9-5-7-10(8-6-9)12(3)4/h5-8H,1-4H3
CJAOGUFAAWZWNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine (TMPDA) is a redox reagent with low ionization potential widely used as an electron donor for photosystem I. It also acts as an electron acceptor in photosystem II.
Applicazioni
N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine (TMPDA) can be used:
- In the flow injection analysis of benzoyl peroxide.
- To study photoinduced electron transfer to halogenated solvents.
Avvertenza
May darken in storage.
Avvertenze
Warning
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
230.0 °F - closed cup
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
110 °C - closed cup
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Ultrafast photoinduced electron transfer from N, N, N′ , N′ -tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine and N, N, N′ , N′ -tetramethylbenzidine to dichloromethane
Boilet L, et al.
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 163(3), 529-536 (2004)
Flow injection analysis of benzoyl peroxide using N, N, N, N-tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine (TMPDA) and surfactants
Pharr DY & Tomsyck JA
Analytical Letters, 42(5), 821-832 (2009)
Interaction of N, N, N′ ,N′ -tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine with photosystem II as revealed by thermoluminescence: reduction of the higher oxidation states of the Mn cluster and displacement of plastoquinone from the QB niche
Gauthier A, et al.
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1757(11), 1547-1556 (2006)
P P Bawol et al.
Physical chemistry chemical physics : PCCP, 20(33), 21447-21456 (2018-08-09)
The reversibility of current Li-O2 batteries suffers from high charging overpotentials. To address this problem, the use of redox mediators has been proposed, which are supposed to improve the sluggish reaction kinetics of the oxygen evolution reaction via a solution
Toshiaki Miura
Chemico-biological interactions, 236, 67-73 (2015-04-30)
To investigate the mechanisms of cardiotoxicity induced by adriamycin (ADM), the enzymatic activities of ADM-Fe(3+), including the peroxidase and lipoxygenase (LOX) activity, and participation of active oxygen species in the damage to biological components were examined. ADM-Fe(3+), but not ADM
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.