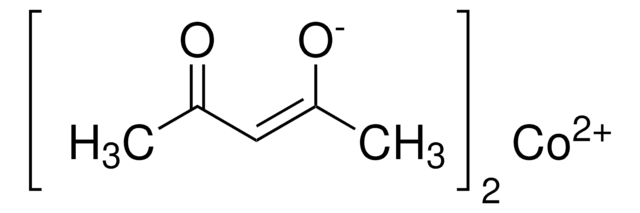
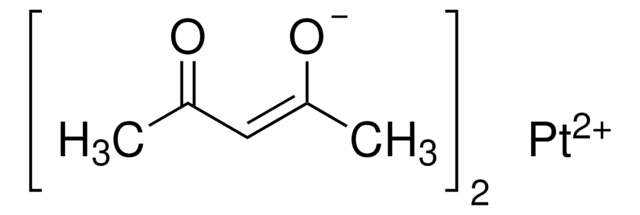
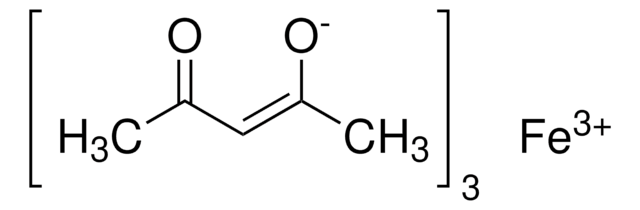
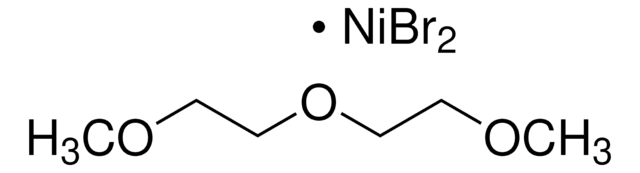
283657
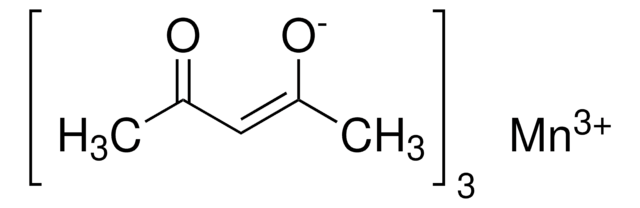
Nickel(II) acetylacetonate
95%
Sinonimo/i:
2,4-Pentanedione nickel(II) derivative, Ni(acac)2
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
95%
Forma fisica
solid
Impiego in reazioni chimiche
core: nickel
reagent type: catalyst
Punto di fusione
230 °C (dec.) (lit.)
Stringa SMILE
CC(=O)\C=C(\C)O[Ni]O\C(C)=C/C(C)=O
InChI
1S/2C5H8O2.Ni/c2*1-4(6)3-5(2)7;/h2*3,6H,1-2H3;/q;;+2/p-2/b2*4-3-;
BMGNSKKZFQMGDH-FDGPNNRMSA-L
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
- Used as a precursor to synthesize Ni-based nanomaterials such as NiO/C nanocomposite and crystalline NiO nanoparticles via different synthetic methods like non-isothermal decomposition and solvothermal method.,·
- Used to prepare Ni catalysts such as Nickel(II) complexes, and hierarchical Ni/beta catalysts for various organictransformations.
- Nickel(II) acetylacetonate has several applications in catalysis: It is used as a catalyst for the polymerization of olefins and transesterification reactions.
- Nickel(II) acetylacetonate can be employed as a catalyst to promote Michael additions.
Prodotti correlati
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Carc. 1A - Muta. 2 - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
428.0 °F
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
220 °C
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.