SRP2017
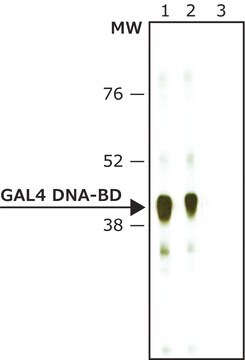
GAL4 [(1-147) + VP16 (411-490)] from Saccharomyces cerevisiae human herpesvirus 2
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, ≥80% (SDS-PAGE)
Sinônimo(s):
VP16
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
fonte biológica
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
human herpesvirus 2
recombinante
expressed in E. coli
Ensaio
≥80% (SDS-PAGE)
forma
frozen liquid
peso molecular
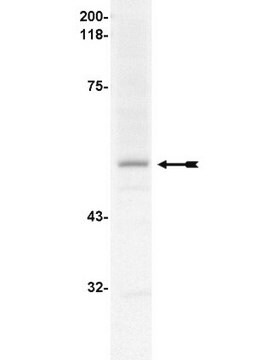
~27.8 kDa
embalagem
pkg of 10 and 500 μg
condição de armazenamento
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
concentração
500 μg/mL
técnica(s)
electrophoretic mobility shift assay: suitable
cor
colorless to clear
nº de adesão NCBI
nº de adesão UniProt
Condições de expedição
dry ice
temperatura de armazenamento
−70°C
Informações sobre genes
Saccharomyces cerevisiae ... GAL4(855828)
human herpesvirus 2 ... HS2VP16A(1487335)
Descrição geral
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
forma física
Nota de preparo
Código de classe de armazenamento
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 1
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Certificados de análise (COA)
Busque Certificados de análise (COA) digitando o Número do Lote do produto. Os números de lote e remessa podem ser encontrados no rótulo de um produto após a palavra “Lot” ou “Batch”.
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica