Descrição geral
MLCK, a member of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family, is a calcium/calmodulin-dependent enzyme responsible for smooth muscle contraction via phosphorylation of a specific serine in the N-terminus of myosin light chains (MLC), an event that facilitates myosin interaction with actin filaments. It is a central determinant in the development of vascular permeability and tissue edema formation. In the nervous system it has been shown to control the growth initiation of astrocytic processes in culture and to participate in transmitter release at synapses formed between cultured sympathetic ganglion cells. MLCK acts as a critical participant in signaling sequences that result in fibroblast apoptosis. Smooth muscle and non-muscle isozymes are expressed in a wide variety of adult and fetal tissues and in cultured endothelium with qualitative expression appearing to be neither tissue- nor development-specific. Non-muscle isoform 2 is the dominant splice variant expressed in various tissues. The Telokin isoform, which binds calmodulin, has been found in a wide variety of adult and fetal tissues. MLCK is probably down-regulated by phosphorylation. The protein contains 1 fibronectin type III domain and 9 immunoglobulin-like C2-type domains.
Myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) is a serine/threonine kinase. It is encoded by the gene mapped to human chromosome 3q21.1. The encoded protein contains an N-terminal actin binding domain, a central kinase domain and C-terminal calmodulin and myosin-binding domains.
Myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) is a serine/threonine kinase, encoded by the gene mapped to human chromosome 3q21.1. The protein contains immunoglobulin (Ig) repeats and fibronectin type 3 like repeats.
Imunogênio
MLCK (Q96DV1, 20-55)
This antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide selected from the N-terminal region of human MLCK.
Aplicação
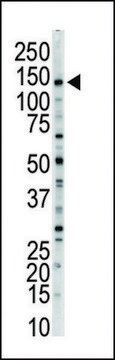
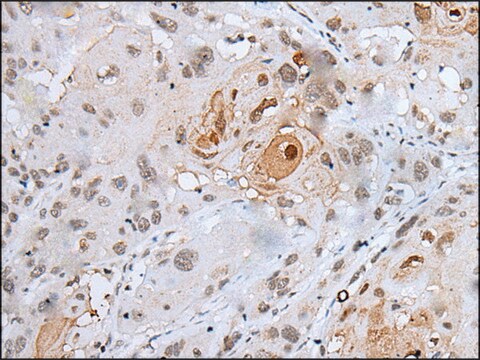
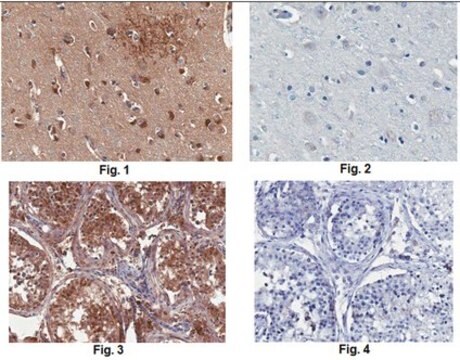
Anti-MLCK (N-term) antibody produced in rabbit has been used in Western blotting.
Anti-MLCK (N-term) antibody produced in rabbit has been used in Western blotting.
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
Myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) is activated by the binding of Ca2+/calmodulin. It has a role in smooth muscle contraction. The kinase phosphorylates the regulatory light chain of smooth muscle myosin. This stimulates ATPase activity of the myosin heads and leads to the myosin power stroke, which is crucial for muscle contraction. MLCK also assists the interaction of myosin with actin. Loss of function of the protein has been linked to megacystis microcolon intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome. In nonmuscle cells, MLCK facilitates various functions such as the maintenance of endothelial cells permeability, stress fiber formation, cell migration, fibroblasts contractile activity and proliferation. It also aids in cytokinesis, secretion, neurite growth cone extension, modulation of ion channel currents. In addition, MLCK is also implicated in signaling pathways leading to fibroblast apoptosis and maintenance of normal cardiac function.
Myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) is activated by the binding of Ca2+/calmodulin. It has a role in smooth muscle contraction. The kinase phosphorylates the regulatory light chain of smooth muscle myosin. This stimulates ATPase activity of the myosin heads and leads to the myosin power stroke, which is crucial for muscle contraction. MLCK also assists the interaction of myosin with actin. Loss of function of the protein has been linked to megacystis microcolon intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome. It facilitates actin binding activity and regulates the actin–myosin interaction.
forma física
Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide.
Exoneração de responsabilidade
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.