N2783
Nitric Oxide Synthase, Inducible from mouse
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, buffered aqueous solution
Sinônimo(s):
Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase, NOS II, iNOS, macNOS
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
recombinante
expressed in E. coli
Nível de qualidade
Formulário
buffered aqueous solution
atividade específica
≥4.0 units/mg protein
peso molecular
130 kDa (homodimer)
130 kDa (subunit, homodimer)
nº de adesão UniProt
Condições de expedição
dry ice
temperatura de armazenamento
−70°C
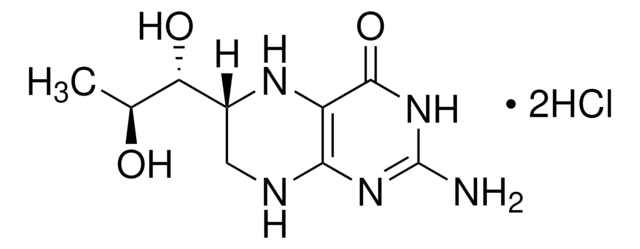
Informações sobre genes
mouse ... Nos2(18126)
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Descrição geral
Aplicação
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
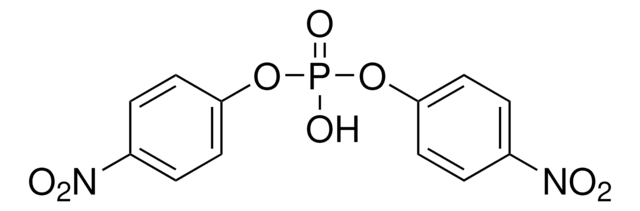
Definição da unidade
forma física
Código de classe de armazenamento
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
early lactation in water buffalo dams
Artigos
Oxidative stress is mediated, in part, by reactive oxygen species produced by multiple cellular processes and controlled by cellular antioxidant mechanisms such as enzymatic scavengers or antioxidant modulators. Free radicals, such as reactive oxygen species, cause cellular damage via cellular.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica