304-05A
Human Aortic Endothelial Cells: HAOEC, adult
Sinônimo(s):
HAOEC cells
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
fonte biológica
human aorta
Nível de qualidade
embalagem
pkg of 500,000 cells
fabricante/nome comercial
Cell Applications, Inc
modo de crescimento
Adherent
cariótipo
2n = 46
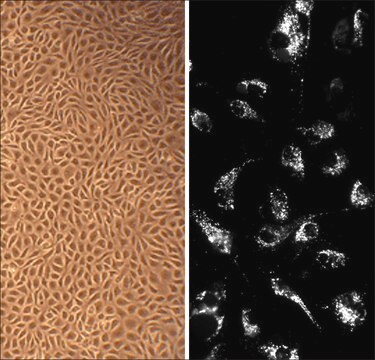
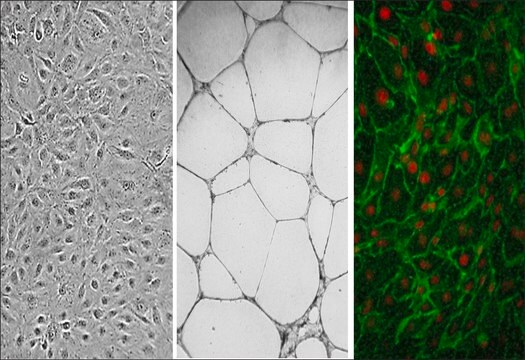
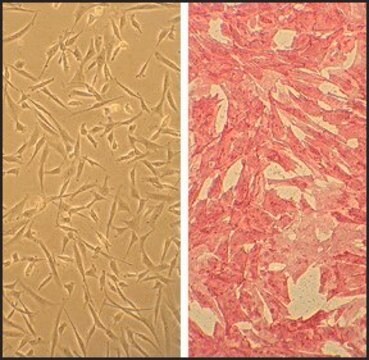
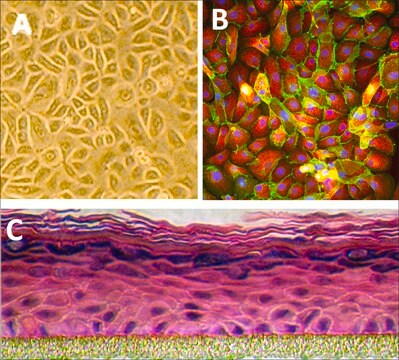
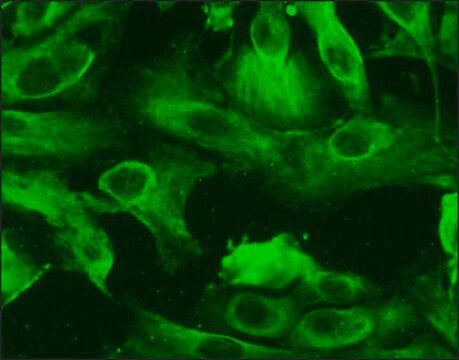
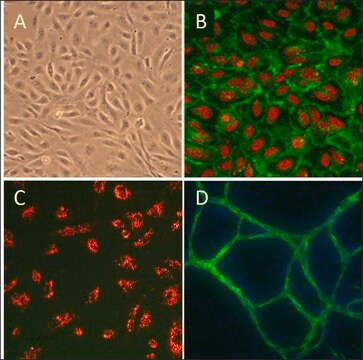
morfologia
Endothelial
técnica(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
doença(s) relevante(s)
diabetes; cardiovascular diseases
Condições de expedição
dry ice
temperatura de armazenamento
−196°C
Descrição geral
Because of the complex heterogeneity that exists not only between different donors, but even between different vascular beds in the same individual, it would be prudent to confirm any new findings on primary cell lots coming from several different origins.
- demonstrate that increased glucose flux leads to endothelial dysfunction in diabetes via activating Egr1-mediated proinflammatory and prothrombotic responses (Vedantham, 2013);
- study apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammation associated with atherosclerosis (Fu, 2014) and demonstrate the beneficial effects of anthocyanin on endothelial cells damaged by exposure to oxidized sterols (Wang, 2012);
- demonstrate that upregulation of thioredoxin via AMPK-FOXO3 pathway protects endothelial cells from oxidative stress and may prevent cardiovascular diseases in patients with metabolic syndrome and diabetes (Li, 2009a,b; Hou, 2010) and further elucidate the involvement of AMPK cascade in mediating beneficial cardiovascular effects of green tea (Reiter, 2010);
- test anti-inflammatory and vasodilating properties of a synthetic rutaecarpine derivative (Lee, 2013);
- show that glycated albumin, associated with diabetic complications, decreases endothelial miR-146a expression which leads to increased IL-6 production, and that angiotensin protects endothelial cells by preventing miR-146a downregulation (Wang, 2013);
- demonstrate that air pollutants can directly affect ZO-1 function leading to increased endothelial permeability, inflammatory cell transmigration and initiation of atherosclerosis (Li, 2010);
- discover the involvement of stress signaling JNK and p38 pathways in pathological suppression of thrombomodulin, a vascular protective molecule, downregulated in many thrombotic and vascular diseases (Rong, 2010);
- link uremic toxins (in particular, PAA) in patients with chronic liver disease to increased ROS production and stimulation of TNF-a in endothelial cells leading to atherosclerosis and vascular calcification (Morita, 2011);
- demonstrate that in diabetes, advanced glycation end products lead to ROS generation in endothelia via sustained NF-kB activation, contributing to progression of atherosclerosis (Morita, 2013);
- discover that CD40 ligand promotes monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells via PKCa, NF-kB and VCAM-1 signaling cascade, explaining the role of CD40L in atherogenesis (Wu, 2013);
- show that monocytes activated by endothelial cells, produce CD80 signaling that leads to allogenic immune response, indicating the need for specific therapy to prevent monocyte activation during allograft transplantation (Wang, 2008);
- identify tetraspanin CD82 as the recognition sensor responsible for rejection of xenotransplants (Saleh, 2013);
- develop 3d endothelialized engineered tissues (Sakai, 2012), as well as new technology based on novel material surfaces and drugs (such as paclitaxel, sirolimus, vitamin C, C6-ceramide and 17?-estradiol) to inhibit smooth muscle cell proliferation at the same time allowing endothelial cells adhesion and proliferation in order to reduce risk associated with vascular implants (Wang, 2009, 2011; Kanie, 2012; Deshpande, 2013; Kakade, 2013; Lamichane, 2013);
Human Aortic Endothelial Cells (HAOEC) provide an excellent model system to study all aspects of cardiovascular function and disease, and they have been utilized in dozens of research publications to study diabetes-associated complications related to cardiovascular function, investigate mechanisms of immune response and graft rejection, study endothelial dysfunction caused by air pollution, oxidative stress and inflammation, and develop 3d endothelialized engineered tissues, as well as new technologies based on novel material surfaces and drugs in order to reduce risks associated with vascular implants.
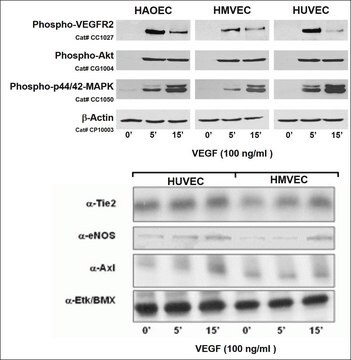
Select HAOEC lots have been additionally tested to demonstrate stimulation-dependent angiogenesis and key endothelial cell signaling pathways (phosphorylation of VEGFR, Akt, MAPK, and expression of Tie2, eNOS, Axl and Etk/Bmx).
Origem de linhagem celular
Aplicação
Componentes
Nota de preparo
- 2nd passage, >500,000 cells in Basal Medium containing 10% FBS & 10% DMSO
- Can be cultured at least 16 doublings
Rotina de subcultura
Exoneração de responsabilidade
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Certificados de análise (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documentos section.
Se precisar de ajuda, entre em contato Atendimento ao cliente
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Protocolos
Human Aortic Endothelial Cells (HAOEC) Culture Protocol
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica