11581074001
Roche
COT Human DNA
from human placenta DNA, enriched for repetitive sequences
Sinônimo(s):
COT Human DNA, Human DNA
Faça loginpara ver os preços organizacionais e de contrato
About This Item
Código UNSPSC:
41106310
Produtos recomendados
fonte biológica
human placenta (DNA)
Nível de qualidade
grau
Molecular Biology
Formulário
solution
embalagem
pkg of 500 μg
fabricante/nome comercial
Roche
concentração
1 mg/mL
Impurezas
HCV/HBV, none detected
HIV 1/2, none detected
cor
colorless
solubilidade
water: miscible
temperatura de armazenamento
−20°C
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Categorias relacionadas
Descrição geral
Repetitive elements (IRS) present in a probe (e.g., cosmids, YACs, chromosome painting probes) generate nonspecific hybridization signals that are distributed over the whole chromosome or genome. To enable specific hybridization of the probe to the chromosomal target site (e.g., single-copy sequences or low-copy repeats) the probe must be denatured in the presence of excess unlabeled COT Human DNA. This DNA serves as a competitor. In a subsequent preannealing step, the repetitive probe elements rapidly hybridize to excess repeats in the COT Human DNA, while most of the specific probe sequences remain single-stranded and thus can be hybridized to their chromosomal targets. This technique is known as chromosomal in situ suppression (CISS) hybridization.
The COT fraction of human genomic DNA consists largely of rapidly annealing repetitive elements. These interspersed repetitive sequences (IRS) such as SINEs (small interspersed repetitive elements, e.g., Alu-elements) and LINEs (large interspersed repetitive elements, e.g., L1-elements) are distributed ubiquitously throughout the genome. COT Human DNA is prepared from human placental DNA by shearing, denaturing, and reannealing under conditions that enrich these repetitive elements.
Aplicação
COT Human DNA is used in chromosome in situ suppression (CISS) hybridization. Cosmid or YAC probes contain repetitive elements that result in monospecific hybridization signals distributed over the entire chromosome. To enable specific hybridization to the chromosomal target site, the probe is denatured together with an excess of unlabeled COT Human DNA as a competitor. COT Human DNA can be used to suppress nonspecific hybridization to human repetitive sequences in microarray analysis, and in filter and in fluorescent in situ hybridization experiments.
Sequência
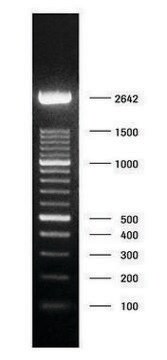
In agarose gel electrophoresis the length distribution of the COT Human DNA fragments shows a maximum in the range of 50 to 300 nucleotides.
forma física
Solution, 1 mg/ml, 10 mM Tris-HCl, 1 mM EDTA, pH 7.4
Outras notas
For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Código de classe de armazenamento
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
nwg
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
No data available
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
No data available
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Early S-phase cell hypersensitivity to heat stress
Nadezhda V
Cell Cycle (2016)
HiCTMap: Detection and Analysis of Chromosome Territory Structure and Position
by High-throughput Imaging
by High-throughput Imaging
Ziad Jowhar
Nature (2017)
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica