05-740
Anti-phospho-ATM (Ser1981) Antibody, clone 10H11.E12
clone 10H11.E12, Upstate®, from mouse
Sinônimo(s):
A-T, mutated, AT mutated, TEL1, telomere maintenance 1, homolog, ataxia telangiectasia mutated, ataxia telangiectasia mutated (includes complementation groups A, C and D), ataxia telangiectasia mutated protein, human phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase homolog
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
fonte biológica
mouse
Nível de qualidade
forma do anticorpo
purified antibody
tipo de produto de anticorpo
primary antibodies
clone
10H11.E12, monoclonal
reatividade de espécies
mouse, human
embalagem
antibody small pack of 25 μg
fabricante/nome comercial
Upstate®
técnica(s)
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunofluorescence: suitable
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
western blot: suitable
Isotipo
IgG1κ
nº de adesão NCBI
nº de adesão UniProt
Condições de expedição
ambient
modificação pós-traducional do alvo
phosphorylation (pSer1981)
Informações sobre genes
human ... ATM(472)
Descrição geral
Especificidade
Imunogênio
Aplicação
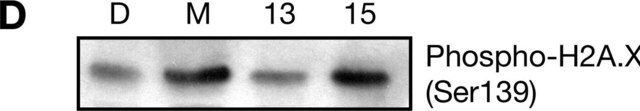
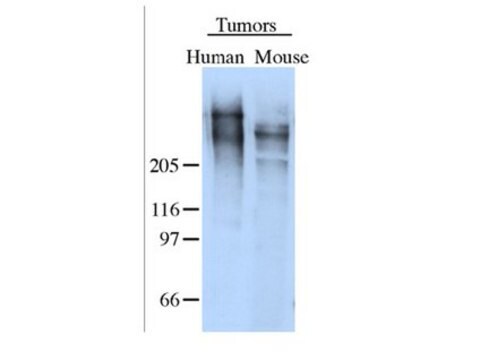
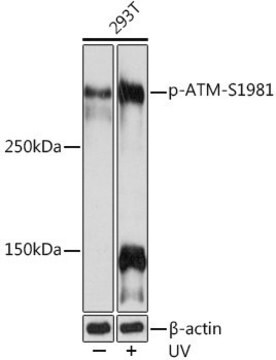
Phosphorylated ATM was immunoprecipitated from irradiated HeLa cells (Figure A, lanes 3 and 4).
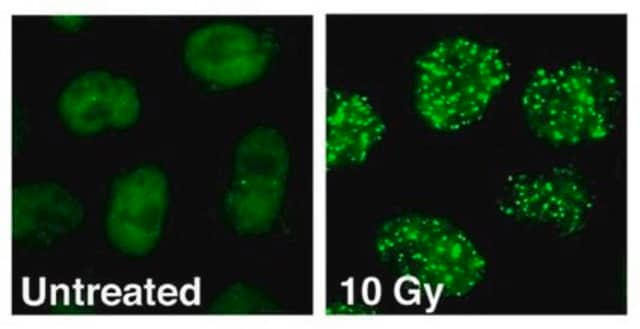
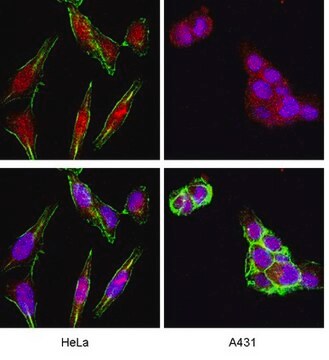
Immunocytochemistry:
Foci are detected in irradiated human and mouse fibroblasts. Determined by an independent laboratory.
Epigenetics & Nuclear Function
Cell Cycle, DNA Replication & Repair
Qualidade
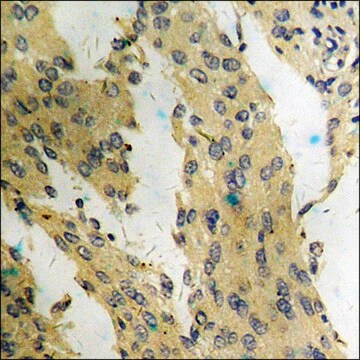
Western Blot Analysis:
0.5 µg/mL of this lot detected phosphorylated ATM in crude lysates from irradiated HeLa cells.
Descrição-alvo
forma física
Armazenamento e estabilidade
Handling Recommendations:
Upon receipt, and prior to removing the cap, centrifuge the vial and gently mix the solution. Aliquot into microcentrifuge tubes and store at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles, which may damage IgG and affect product performance. Note: Variability in freezer temperatures below -20°C may cause glycerol containing solutions to become frozen during storage.
Nota de análise
Irradiated HeLa cell lysates
Outras notas
Informações legais
Exoneração de responsabilidade
Não está encontrando o produto certo?
Experimente o nosso Ferramenta de seleção de produtos.
recomendado
Código de classe de armazenamento
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 1
Certificados de análise (COA)
Busque Certificados de análise (COA) digitando o Número do Lote do produto. Os números de lote e remessa podem ser encontrados no rótulo de um produto após a palavra “Lot” ou “Batch”.
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica