759406
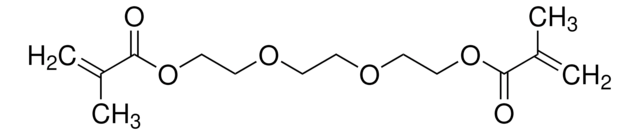
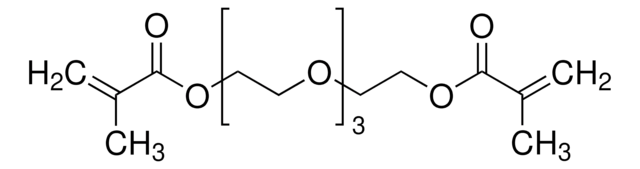
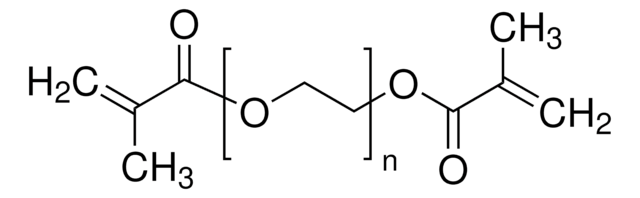
Triethylene glycol dimethacrylate
99%, cross-linking reagent polymerization reactions, 200 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
product name
Triethylene glycol dimethacrylate, contains 200 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor, 99%
Nível de qualidade
Ensaio
99%
forma
liquid
contém
200 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor
adequação da reação
reagent type: cross-linking reagent
reaction type: Polymerization Reactions
índice de refração
n20/D 1.461 (lit.)
n/D 1.4613
pb
170-172 °C/5 mmHg (lit.)
densidade
1.092 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
1.074 g/mL
arquitetura do polímero
shape: linear
functionality: homobifunctional
temperatura de armazenamento
2-8°C
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
CC(=C)C(=O)OCCOCCOCCOC(=O)C(C)=C
InChI
1S/C14H22O6/c1-11(2)13(15)19-9-7-17-5-6-18-8-10-20-14(16)12(3)4/h1,3,5-10H2,2,4H3
chave InChI
HWSSEYVMGDIFMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Descrição geral
Aplicação
- Used as a diluent comonomer in dimethacrylate based dental composites.
- Used as a branching agent in the atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) of styrene.
Características e benefícios
Palavra indicadora
Warning
Frases de perigo
Declarações de precaução
Classificações de perigo
Skin Sens. 1
Código de classe de armazenamento
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 1
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
332.6 °F - closed cup
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
167 °C - closed cup
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Certificados de análise (COA)
Não está vendo a versão correta?
Se precisar de uma versão específica, você pode procurar um certificado específico pelo número do lote ou da remessa.
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica