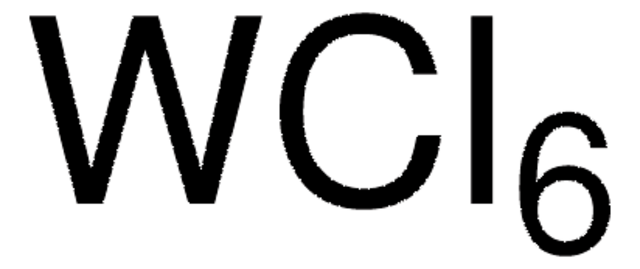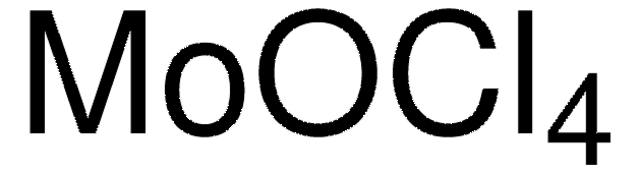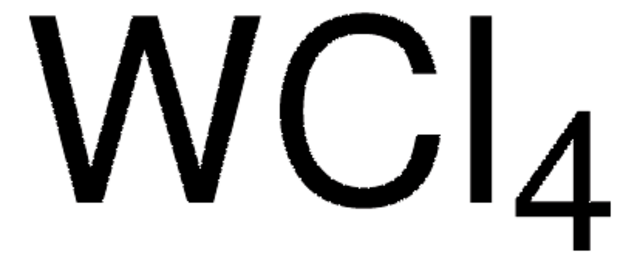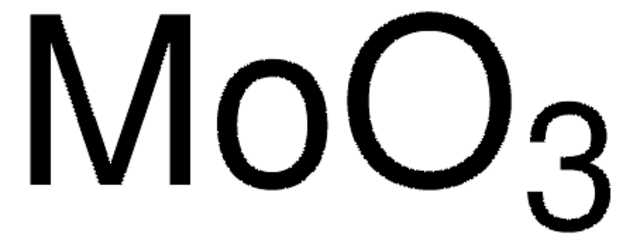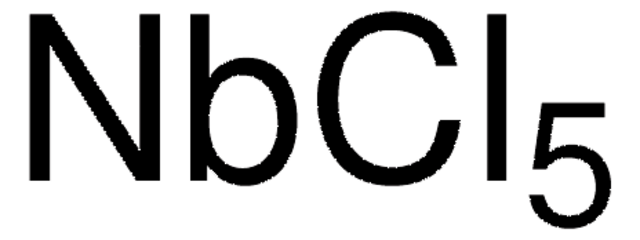642452
Molybdenum(V) chloride
anhydrous, powder, 99.99% trace metals basis (excluding W)
Sinônimo(s):
Molybdenum pentachloride, Molybdenum(5+) chloride
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
grau
anhydrous
Nível de qualidade
pressão de vapor
1.75 mmHg ( 25 °C)
131 mmHg ( 250 °C)
Ensaio
99.99% trace metals basis (excluding W)
Formulário
powder
Impurezas
≤150.0 ppm Trace Metal Analysis
p.e.
268 °C (lit.)
pf
194 °C (lit.)
densidade
2.928 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
aplicação(ões)
battery manufacturing
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
Cl[Mo](Cl)(Cl)(Cl)Cl
InChI
1S/5ClH.Mo/h5*1H;/q;;;;;+5/p-5
chave InChI
GICWIDZXWJGTCI-UHFFFAOYSA-I
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Categorias relacionadas
Descrição geral
Aplicação
- As a catalyst for amidation of secondary benzyl alcohols.
- As a precursor to fabricate MoS2 thin films by atomic layer deposition method.
- As a primary catalyst for coordination polymerization of butadiene.
- To fabricate superior anode materials for Na-ion and Li-ion batteries.
- As a dual-function redox mediator for Li–O2 batteries to overcome thehigh polarization and low energy density issues.
acessório
Palavra indicadora
Danger
Frases de perigo
Declarações de precaução
Classificações de perigo
Skin Corr. 1B
Código de classe de armazenamento
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Equipamento de proteção individual
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Artigos
Nanostructured Materials Through Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis
We presents an article about a micro review of reversible addition/fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization. RAFT (Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
Applying ARGET ATRP to the Growth of Polymer Brush Thin Films by Surface-initiated Polymerization
We presents an article about Copper(I)-mediated Living Radical Polymerization in the Presence of Pyridylmethanimine Ligands, and the emergence of living radical polymerization mediated by transition metal catalysts in 1995, which was a seminal piece of work in the field of synthetic polymer chemistry.
Protocolos
We presents an article featuring procedures that describe polymerization of methyl methacrylate and vinyl acetate homopolymers and a block copolymer as performed by researchers at CSIRO.
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about RAFT, or Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer, which is a form of living radical polymerization.
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about the typical procedures for polymerizing via ATRP, which demonstrates that in the following two procedures describe two ATRP polymerization reactions as performed by Prof. Dave Hadddleton′s research group at the University of Warwick.
Conteúdo relacionado
We offer a complete line of the highest purity inorganic salts and materials for the micro and nanoelectronics market.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica