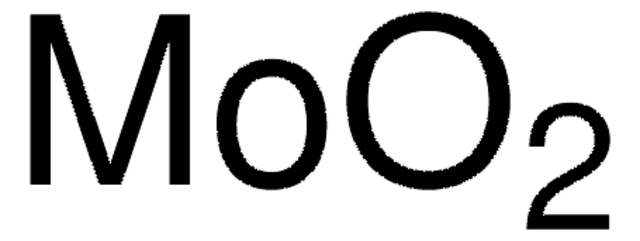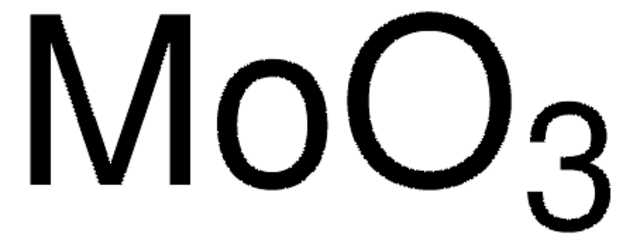203815
Molybdenum(VI) oxide
99.97% trace metals basis
Sinônimo(s):
Molybdenum trioxide
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
Ensaio
99.97% trace metals basis
Formulário
powder
pf
795 °C (lit.)
aplicação(ões)
battery manufacturing
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
O=[Mo](=O)=O
InChI
1S/Mo.3O
chave InChI
JKQOBWVOAYFWKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Descrição geral
Aplicação
Palavra indicadora
Warning
Frases de perigo
Declarações de precaução
Classificações de perigo
Carc. 2 - Eye Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Órgãos-alvo
Respiratory system
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 1
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Equipamento de proteção individual
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Artigos
Nanostructured Materials Through Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis
The production of hydrogen by catalytic water splitting is important for a wide range of industries including renewable energy petroleum refining and for the production of methanol and ammonia in the chemical industry.
Professor Chen (Nankai University, China) and his team explain the strategies behind their recent record-breaking organic solar cells, reaching a power conversion efficiency of 17.3%.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica