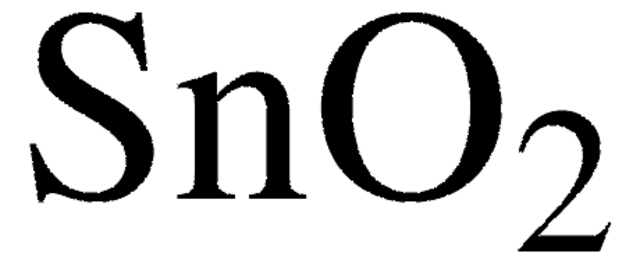244651
Tin(IV) oxide
−325 mesh, 99.9% trace metals basis
Sinônimo(s):
Stannic oxide
Faça loginpara ver os preços organizacionais e de contrato
About This Item
Fórmula linear:
SnO2
Número CAS:
Peso molecular:
150.71
Número CE:
Número MDL:
Código UNSPSC:
12352303
ID de substância PubChem:
NACRES:
NA.23
Produtos recomendados
Ensaio
99.9% trace metals basis
Formulário
powder
tamanho de partícula
−325 mesh
densidade
6.95 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
aplicação(ões)
battery manufacturing
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
O=[Sn]=O
InChI
1S/2O.Sn
chave InChI
XOLBLPGZBRYERU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Categorias relacionadas
Descrição geral
Tin(IV) oxide (SnO2) is an n-type wide band gap semiconductor with high transmittance at nearIR and visible region. It is scratch resistant and chemically inert.
Aplicação
Tin(IV) oxide has been used to prepare thin films of TiO2-doped SnO2 oxide nanocomposites.
It can be used as astarting material to prepare niobium and zinc-doped titanium-tin-oxidesolid-solution ceramics, which are applicable in the field of electronicdevices.
It can be used as astarting material to prepare niobium and zinc-doped titanium-tin-oxidesolid-solution ceramics, which are applicable in the field of electronicdevices.
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
nwg
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Equipamento de proteção individual
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Gun-Joo Sun et al.
Nanotechnology, 24(2), 025504-025504 (2012-12-15)
Networked SnO(2) nanowire sensors were achieved using the selective growth of SnO(2) nanowires and their tangling ability, particularly on on-chip V-groove structures, in an effort to overcome the disadvantages imposed on the conventional trench-structured SnO(2) nanowire sensors. The sensing performance
Li-Ping Li et al.
Chemical communications (Cambridge, England), 49(17), 1762-1764 (2013-01-25)
ZnSn(OH)(6) and binary-component SnO(2)-ZnSn(OH)(6) were introduced as affinity probes for phosphopeptide enrichment for the first time. Two strategies, either ZnSn(OH)(6) and SnO(2) serial enrichment or binary-component SnO(2)-ZnSn(OH)(6) enrichment in a single run, were proposed to enhance multi-phosphopeptide enrichment and to
Dawei Su et al.
Chemical communications (Cambridge, England), 49(30), 3131-3133 (2013-03-13)
An in situ hydrothermal synthesis approach has been developed to prepare SnO2@graphene nanocomposites. The nanocomposites exhibited a high reversible sodium storage capacity of above 700 mA h g(-1) and excellent cyclability for Na-ion batteries. In particular, they also demonstrated a
Linlin Li et al.
Nanoscale, 5(1), 134-138 (2012-11-14)
Novel eggroll-like CaSnO(3) nanotubes have been prepared by a single spinneret electrospinning method followed by calcination in air for the first time. The electrospun sample as a lithium-ion battery electrode material exhibited improved cycling stability and rate capability by virtue
Yinzhu Jiang et al.
ACS applied materials & interfaces, 4(11), 6216-6220 (2012-10-31)
Porous SnO₂/graphene composite thin films are prepared as anodes for lithium ion batteries by the electrostatic spray deposition technique. Reticular-structured SnO₂ is formed on both the nickel foam substrate and the surface of graphene sheets according to the scanning electron
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica