Wichtige Dokumente
K0250
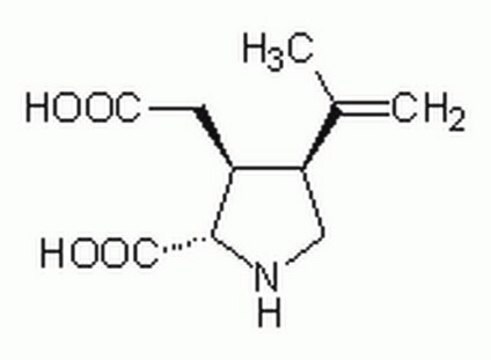
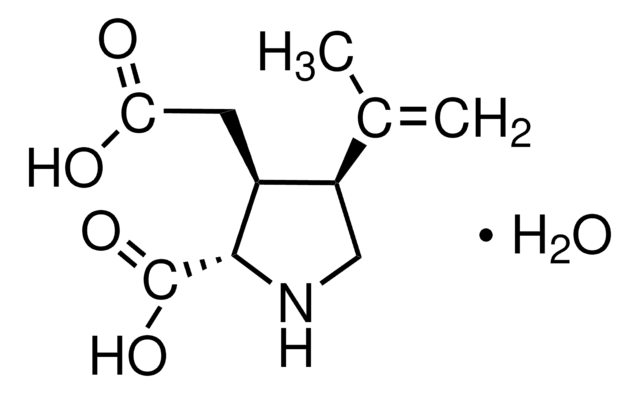
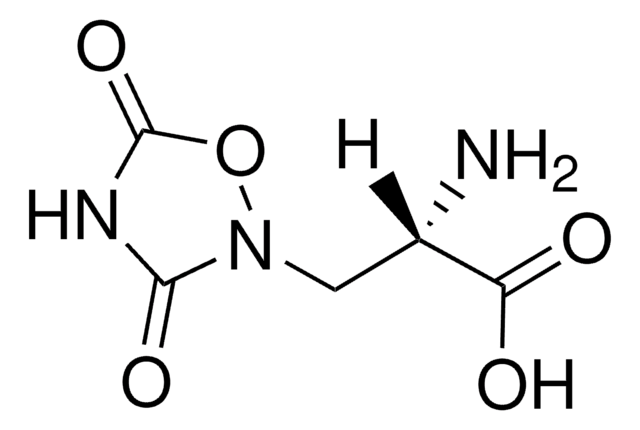
Kainic acid monohydrate
≥99% (TLC), powder, ionotropic glutamate receptor (kainate class) agonist
Synonym(e):
Digenin, Kainate, 2-Carboxy-3-carboxymethyl-4-isopropenylpyrrolidine
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Produktbezeichnung
Kainic acid monohydrate, ≥99% (TLC)
Qualitätsniveau
Assay
≥99% (TLC)
Form
powder
Verunreinigungen
Glutamate, free
Löslichkeit
H2O: soluble
Lagertemp.
2-8°C
SMILES String
O.CC(=C)[C@H]1CN[C@@H]([C@H]1CC(O)=O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C10H15NO4.H2O/c1-5(2)7-4-11-9(10(14)15)6(7)3-8(12)13;/h6-7,9,11H,1,3-4H2,2H3,(H,12,13)(H,14,15);1H2/t6-,7+,9-;/m0./s1
InChIKey
FZNZRJRSYLQHLT-SLGZUKMRSA-N
Angaben zum Gen
human ... GRIA1(2890) , GRIA2(2891) , GRIA4(2893) , GRIK1(2897) , GRIK2(2898) , GRIK3(2899) , GRIK4(2900) , GRIK5(2901) , SLC1A1(6505) , SLC1A2(6506) , SLC1A3(6507)
mouse ... Gria1(14799)
rat ... Gria1(50592) , Grik1(29559) , Grik4(24406) , Grin2a(24409)
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
- tostudy mechanisms of excitation-induced apoptosis and epilepsy.
- to hamper themitochondrial function ()
- used to induce c-fosexpression in the mice′s brains, specifically targeting the dorsal hippocampus.()
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
Leistungsmerkmale und Vorteile
Angaben zur Herstellung
Ähnliches Produkt
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.