42602
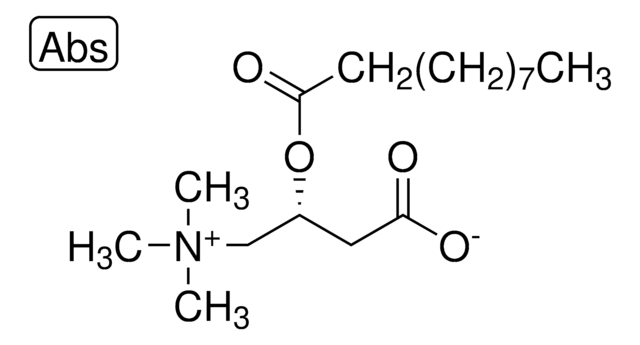
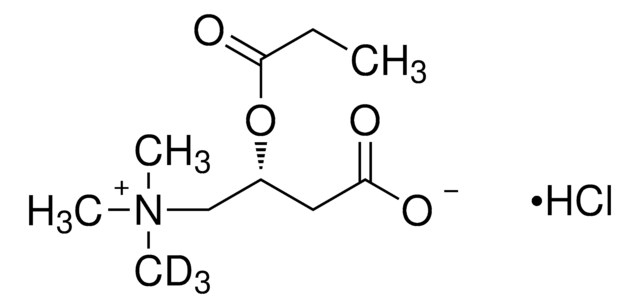
Propionyl-L-carnitin
≥94.0% (HPLC), suitable for LC/MS
Synonym(e):
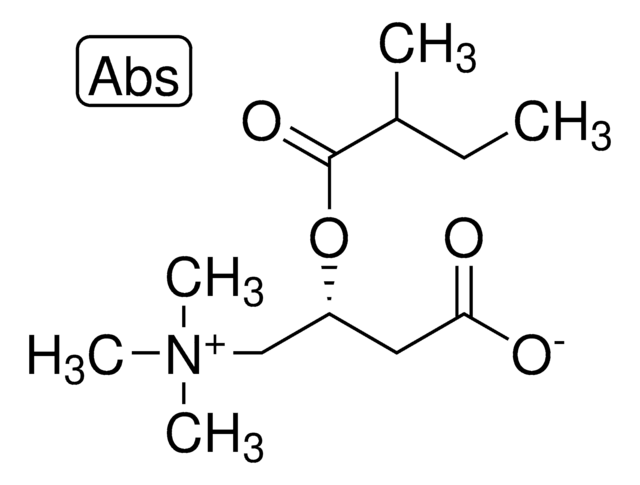
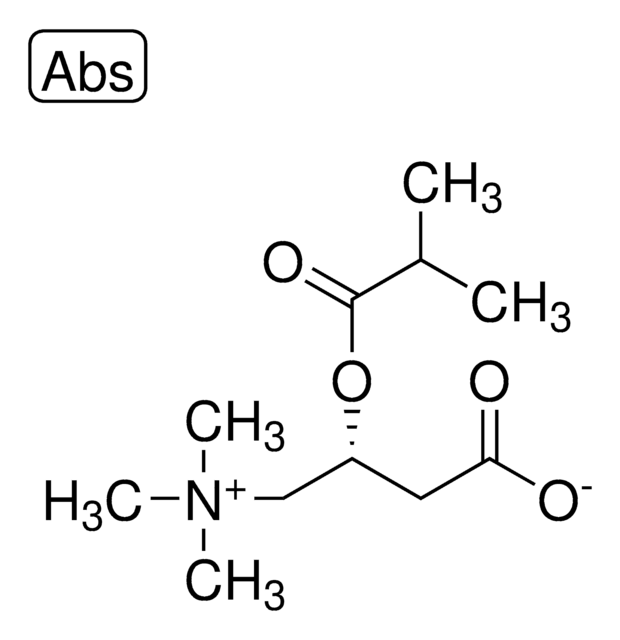
(2R)-3-Carboxy-N,N,N-trimethyl-2-(1-oxopropoxy)-1-propanaminium Inneres Salz, L-Carnitin-propionylester, C3-Carnitin, Propanoyl-L-carnitin
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
product name
Propionyl-L-carnitin, ≥94.0% (HPLC)
Qualitätsniveau
Assay
≥94.0% (HPLC)
Form
powder or crystals
Optische Aktivität
[α]/D -23±3°, c = 1 in H2O
Methode(n)
LC/MS: suitable
Verunreinigungen
≤10% water (calcd. from elemental analysis)
Farbe
white to off-white
Lagertemp.
2-8°C
SMILES String
[O-]C(C[C@@H](OC(CC)=O)C[N+](C)(C)C)=O
InChI
1S/C10H19NO4/c1-5-10(14)15-8(6-9(12)13)7-11(2,3)4/h8H,5-7H2,1-4H3/t8-/m1/s1
InChIKey
UFAHZIUFPNSHSL-MRVPVSSYSA-N
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.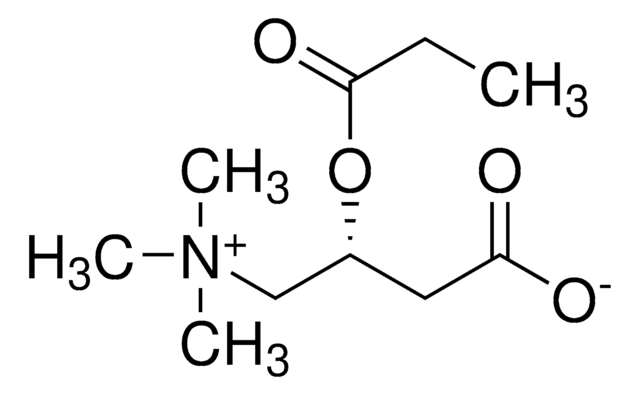
![[(3R)-3-Hydroxybutyryl]-L-carnitin analytical standard](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/658/500/ff9570f8-a346-4077-9983-d0e67400bf47/640/ff9570f8-a346-4077-9983-d0e67400bf47.png)