SML3410
EMD638683
≥98% (HPLC)
Synonym(s):
EMD 638683, EMD-638683, N′-[2-(3,5-Difluorophenyl)-2-hydroxyacetyl]-2-ethyl-4-hydroxy-3-methylbenzohydrazide
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C18H18F2N2O4
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
364.34
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
Recommended Products
Quality Level
assay
≥98% (HPLC)
form
powder
color
white to beige
solubility
DMSO: 2 mg/mL, clear
storage temp.
-10 to -25°C
SMILES string
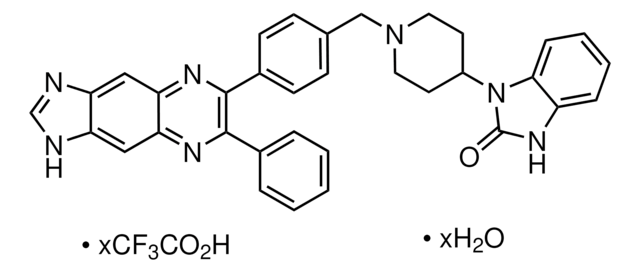
CC1=C(C(C(NNC(C(C2=CC(F)=CC(F)=C2)O)=O)=O)=CC=C1O)CC
Biochem/physiol Actions
EMD638683 is an orally active and highly selective serum/glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 (SGK1) inhibitor (IC50 = 3 μM against HeLa cellular NDRG1 phosphorylation) that significantly decreased blood pressure in fructose-treated mice but not in control saline-treated or in SGK1-knockout animals (4460 ppm in chow, ~600 mg/kg/day). EMD638683 promotes radiation-induced suicidal death of CaCo-2 colon tumor cells in vitro (50 μM) and decreases the number of colonic tumors following chemical carcinogenesis in vivo (4460 ppm in chow).
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
SGK1.1 limits brain damage after status epilepticus through M current-dependent and independent mechanisms
Neurobiology of Disease, 153, 105317-105317 (2021)
EMD638683, a novel SGK inhibitor with antihypertensive potency
Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 28(1), 137-146 (2011)
An increase in alveolar fluid clearance induced by hyperinsulinemia in obese rats with LPS-induced acute lung injury
Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology, 279279, 103470-103470 (2020)
Joshua A Mason et al.
Cell reports, 34(11), 108821-108821 (2021-03-18)
Loss of integrin-mediated attachment to extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins can trigger a variety of cellular changes that affect cell viability. Foremost among these is the activation of anoikis, caspase-mediated cell death induced by ECM detachment. In addition, loss of ECM
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service