P4404
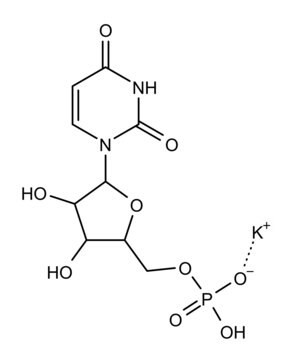
Polyguanylic acid potassium salt
lyophilized powder
Synonym(s):
Poly(G) potassium salt
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
enzyme from (synthesis)
Quality Level
assay
≥95% (TLC)
form
lyophilized powder
quality
≤5% free nucleotides
solubility
water: 19.60-20.40 mg/mL, clear to slightly hazy, colorless to light yellow
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Polyguanylic acid takes up a four-stranded helical structure. It is synthetically produced in Thermus thermophilus from guanosine diphosphate (GDP) and its synthesis is catalyzed by the enzyme polynucleotide phosphorylase.
Application
Polyguanylic acid (PolyG) is used to study the effects of ionizing radiation on formation and stability of G-quadruplex structures and as a target molecule for physicochemical studies of electronic excitation (vibrational spectra) of guanosine.
Polyguanylic acid potassium salt has been used:
- as a ligand for surface neuropilin-1 (NRP1) for internalization studies
- for intercalation studies with trisubstituted and disubstituted triazole-linked phenyl derivatives CL41, CL42 and CL2r50 using voltammetry method
- as a synthetic polynucleotide for agarose gel electrophoresis analysis
Biochem/physiol Actions
Polyguanylic acid acts as a ligand for scavenger receptor and reduces the surface expression neuropilin-1 in endothelial cells.
Preparation Note
Prepared from GDP using polynucleotide phosphorylase
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Venugopal Karunakaran et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 131(16), 5839-5850 (2009-04-04)
Guanosine monophosphate (GMP) in aqueous solutions has been studied with femtosecond broad-band transient absorption spectroscopy and by quantum-mechanical calculations. The sample was excited at 267 or 287 nm and probed between 270 and 1000 nm with 100 fs resolution, for
Zhong-yuan Kan et al.
Nucleic acids research, 35(11), 3646-3653 (2007-05-10)
Chromosomes in vertebrates are protected at both ends by telomere DNA composed of tandem (TTAGGG)n repeats. DNA replication produces a blunt-ended leading strand telomere and a lagging strand telomere carrying a single-stranded G-rich overhang at its end. The G-rich strand
Picosecond infrared probing of the vibrational spectra of transients formed upon UV excitation of stacked G-tetrad structures.
McGovern DA, Quinn S, Doorley GW, et al.
Chemical Communications (Cambridge, England), 28, 5158-5160 (2007)
D Grygoryev et al.
Radiation research, 173(1), 110-118 (2010-01-01)
The ability of guanine-rich sequences to form quadruplex structures in telomeres for example is important in a number of biological processes such as aging, carcinogenesis and gene regulation. Ionizing radiation can cause damage to guanine moieties that can affect the
A study of the pH dependence of electronically excited guanosine compounds by picosecond time-resolved infrared spectroscopy.
McGovern DA, Doorley GW, et al.
Photochemistry and Photobiology, 8, 542-548 (2008)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service