C1805
Anti-CD4 antibody, Mouse monoclonal
clone Q4120, purified from hybridoma cell culture
Synonym(s):
Anti-CD4 antibody, Mouse monoclonal
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352203
NACRES:
NA.41
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
purified from hybridoma cell culture
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
Q4120, monoclonal
form
buffered aqueous solution
mol wt
59 kDa
species reactivity
human
technique(s)
flow cytometry: 5 μL using 1 × 106 cells
isotype
IgG1
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
2-8°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... CD4(920)
Related Categories
General description
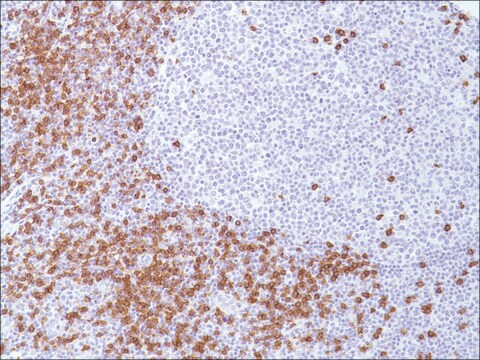
Monoclonal Anti-Human CD4 (mouse IgG1 isotype) is derived from the hybridoma produced by the fusion of mouse myeloma cell line NS-1 and splenocytes from Balb/c mice immunized with CD4-Transfected mouse T-cell hybridoma, 3DT, followed by CD4+ human T-cell CEM cells. Cluster of differentiation 4 (CD4) human cell surface glycoprotein (59kDa) belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is expressed on the helper/inducer T cell subset, which is found on the majority of peripheral blood neutrophils, most cortical and mature medullary thymocytes, microglial cells, dendritic cells and on some malignancies of T cell origin.
Specificity
Recognizes the CD4. The epitope recognized by the Q4120 clone is located on 1-183 aa and is sensitive to formalin fixation and paraffin embedding. 5th Workshop: code no. CD04.11
Immunogen
CD4-transfected mouse T-cell hybridoma, 3DT, followed by CD4+ human T-cell CEM cells.
Application
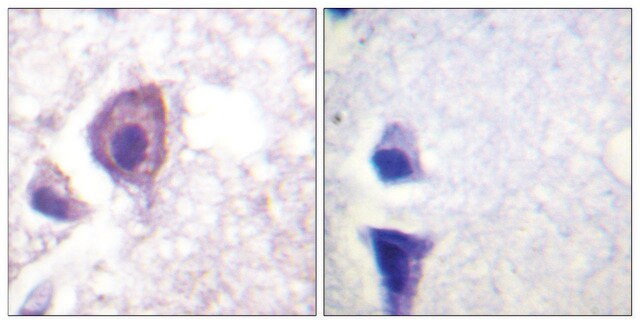
Monoclonal Anti-CD4 antibody produced in mouse has been used in indirect immunofluorescent staining.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cluster of differentiation 4 (CD4) molecule binds to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules during the interaction of CD4+ T cells with antigen presenting cells or with target cells. It also serves as a high affinity cellular receptor for the GP 120 envelope glycoprotein of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1, HIV-2). The CD4 molecule is involved in the adhesion of T-lymphocytes to target cells, thymic development, transmission of intracellular signals during T cell activation, and binding to polyclonal immunoglobulins. Lower levels of CD4 have been detected in monocytes, macrophages and granulocytes.
Target description
CD4 is a single chain transmembraneous glycoprotein from the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is expressed on the helper/inducer T subset, on most medullary thymocytes, on microglial, dendritic and on some malignancies of T cell origin. The antigen binds to MHC class II molecules and is associated with p56lck protein tyrosine kinase.
Physical form
Solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 1% bovine serum albumin and 15 mM sodium azide.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
wgk_germany
nwg
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Functional epitope analysis of the human CD4 molecule: antibodies that inhibit human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gene expression bind to the immunoglobulin CDR3-like region of CD4.
Benkirane M, et al.
Journal of virology, 69(11), 6898-6903 (1995)
CD4+ T cells: differentiation and functions
Luckheeram RV, et al.
Clinical & Developmental Immunology (2012)
Down regulation of CD4 expression following isolation and culture of human monocytes
Graziani-Bowering GM and Filion LG
Clinical and Diagnostic Laboratory Immunology, 7(2), 182-191 (2000)
Taha Hirbod et al.
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950), 191(7), 3948-3954 (2013-09-06)
Studies using genital tissue samples from HIV-infected women might provide important information about HIV susceptibility and transmission. In this study, ectocervical biopsies were obtained from 20 HIV-seropositive (HIV(+)) Kenyan female sex workers (FSW) and 20 HIV-seronegative lower risk (HIV(-) LR)
Expression of CD4 on human peripheral blood neutrophils
Biswas P, et al.
Blood, 101(11), 4452-4456 (2003)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service