323764
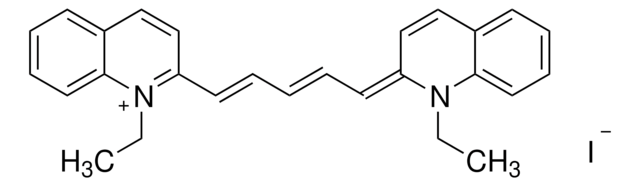
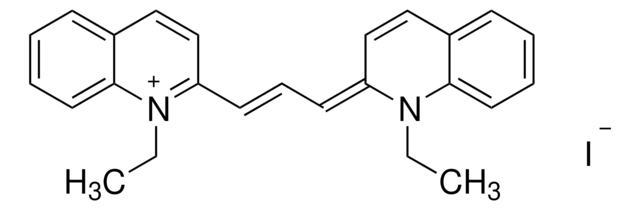
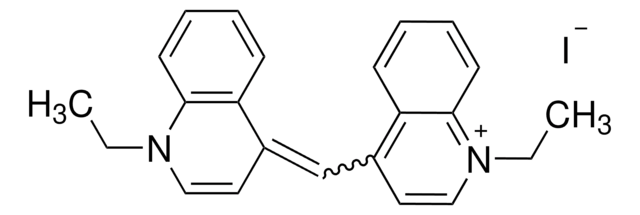
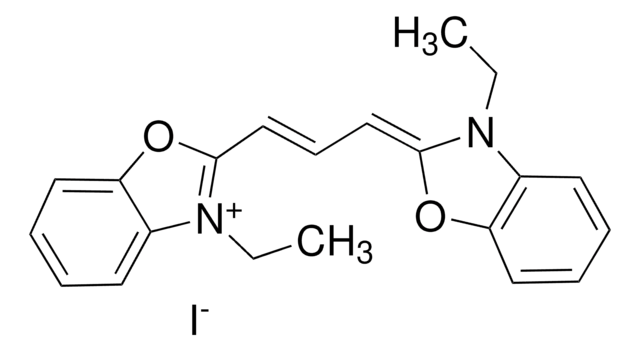
1,1′-Diethyl-2,2′-cyanine iodide
97%
Synonym(s):
1-Ethyl-2-[(1-ethyl-2(1H)-quinolinylidene)methyl]quinolinium iodide, Decynium 22, Pseudocyanine iodide, Pseudoisocyanine iodide
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
assay
97%
form
powder or crystals
mp
273 °C (dec.) (lit.)
λmax
524 nm
ε (extinction coefficient)
≥25000 at 487-495 nm in ethanol
application(s)
diagnostic assay manufacturing
hematology
histology
storage temp.
room temp
SMILES string
[I-].CCN1\C(C=Cc2ccccc12)=C\c3ccc4ccccc4[n+]3CC
InChI
1S/C23H23N2.HI/c1-3-24-20(15-13-18-9-5-7-11-22(18)24)17-21-16-14-19-10-6-8-12-23(19)25(21)4-2;/h5-17H,3-4H2,1-2H3;1H/q+1;/p-1
InChI key
GMYRVMSXMHEDTL-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Related Categories
General description
Application
signalword
Danger
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 2 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 2 Oral - Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
target_organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service