715298
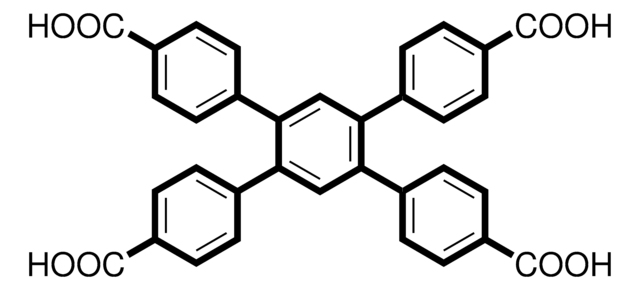
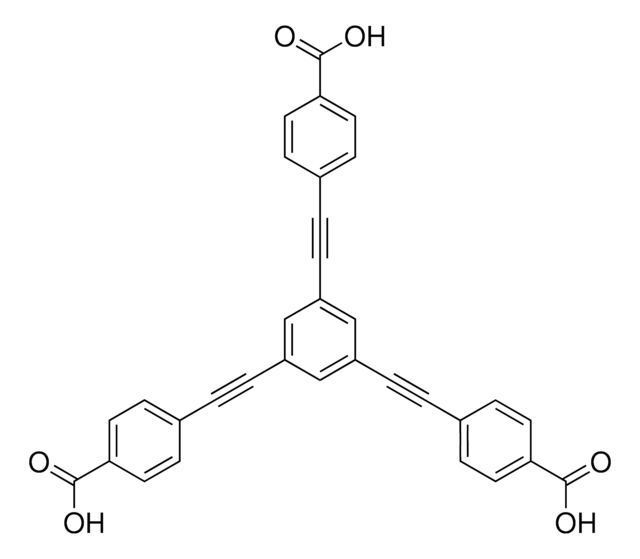
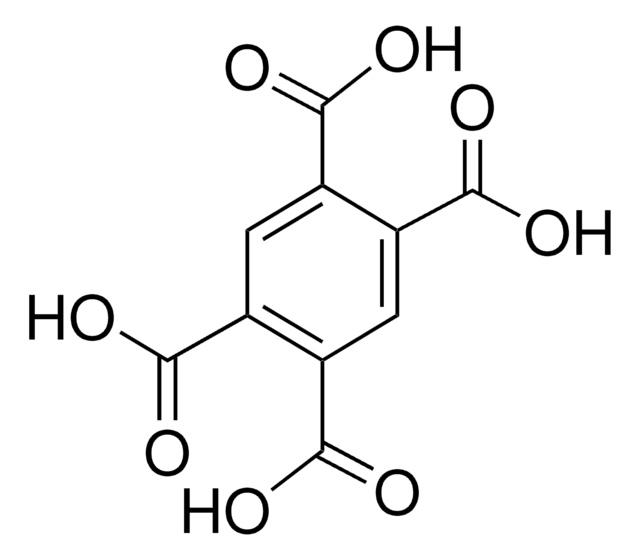
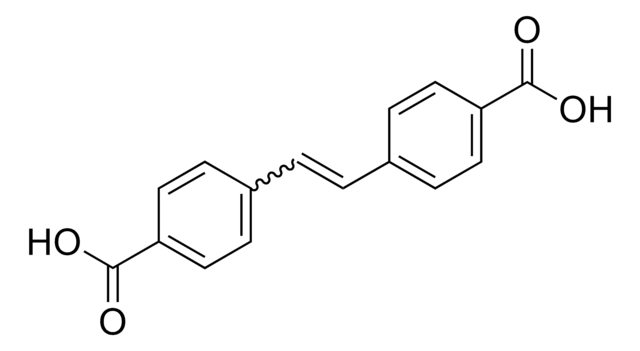
1,2,4,5-Tetrakis(4-carboxyphenyl)benzene
contains up to 6 wt. % water, ≥98%
Synonym(s):
4,4′,4′′,4′′′-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetrayltetrabenzoic acid, H4TCPB
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
assay
≥98%
form
powder
greener alternative product characteristics
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
greener alternative category
SMILES string
OC(=O)c1ccc(cc1)-c2cc(-c3ccc(cc3)C(O)=O)c(cc2-c4ccc(cc4)C(O)=O)-c5ccc(cc5)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C34H22O8/c35-31(36)23-9-1-19(2-10-23)27-17-29(21-5-13-25(14-6-21)33(39)40)30(22-7-15-26(16-8-22)34(41)42)18-28(27)20-3-11-24(12-4-20)32(37)38/h1-18H,(H,35,36)(H,37,38)(H,39,40)(H,41,42)
InChI key
SRTQKANXPMBQCX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
General description
Application
- the formation of supramolecular heterostructures to functionalize black phosphorus
- synthesis of microporous metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for potential usage in hydrogen storage, gas separation, and catalysis.
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
185.0 °F - closed cup
flash_point_c
85 °C - closed cup
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Metal-organic frameworks, a subset of coordination polymers, represent a powerful new tool for a plethora of alternative energy applications. MOFs are readily available using simple synthetic strategies that supply tailored, high surface area materials.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service