325333
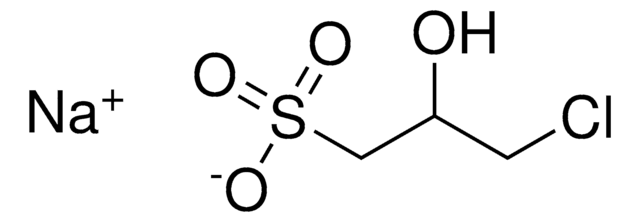
3-Chloro-2-hydroxy-1-propanesulfonic acid sodium salt hydrate
95%
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
ClCH2CH(OH)CH2SO3Na · xH2O
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
196.59 (anhydrous basis)
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
assay
95%
mp
256 °C (dec.) (lit.)
functional group
chloro
sulfonic acid
SMILES string
O.[Na+].OC(CCl)CS([O-])(=O)=O
InChI
1S/C3H7ClO4S.Na.H2O/c4-1-3(5)2-9(6,7)8;;/h3,5H,1-2H2,(H,6,7,8);;1H2/q;+1;/p-1
InChI key
ZPFGAXXLEFTBEU-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
3-Chloro-2-hydroxy-1-propanesulfonic acid sodium salt hydrate is a novel anionic agent.
Application
3-Chloro-2-hydroxy-1-propanesulfonic acid sodium salt hydrate was used:
- to prepare negatively charged probe particles to investigate effect of nanoporosity of cellulosic fibers on their streaming potential and their interactions with cationic polyelectrolytes
- to prepare surface-derivatized microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) particles having either a strong positive or a strong negative zeta potential
signalword
Warning
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
target_organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Consequences of the nanoporosity of cellulosic fibers on their streaming potential and their interactions with cationic polyelectrolytes.
Hubbe MA, et al.
Cellulose, 14(6), 655-671 (2007)
Charge and the dry-strength performance of polyampholytes: Part 2. Colloidal effects.
Hubbe MA, et al.
Colloids and Surfaces. A, Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 301(1), 23-32 (2007)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service