General description
Horseradish peroxidase is isolated from horseradish roots (Amoracia rusticana) and belongs to the ferroprotoporphyrin group of peroxidases. HRP is a single chain polypeptide containing four disulfide bridges. It is a glycoprotein containing 18% carbohydrate. The carbohydrate composition consists of galactose, arabinose, xylose, fucose, mannose, mannosamine, and galactosamine depending upon the specific isozyme. Its molecular weight (~44 kDa) includes the polypeptide chain (33,890 Daltons), hemin plus Ca2+ (~700 Daltons), and carbohydrate (~9,400 Daltons). At least seven isozymes of HRP exist. The isoelectric point for horseradish peroxidase isozymes ranges from 3.0 - 9.0.
Application
Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) is isolated from horseradish roots (Amoracia rusticana). It is used in biochemistry applications such as western blots, ELISA and Immunohistochemistry. Horseradish peroxidase is used to amplify a weak signal and increase detectability of a target molecule, such as a protein. Product P6782 is type VI-A and it is essentially a salt-free, lyophilized powder. It is used to quantify cholesterol and cholesterol esters and to study in vitro lipid deposition on hydrogel and silicone hydrogel contact lenses.
The enzyme from Sigma has been used in the development of rapid and sensitive galactose oxidase-peroxidase biosensor for galactose detection with prolonged stability. It has been used as a component of a media (MRS agar) plate containing 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) for the growth of Lactobacillus sp. TMB acts as a chromogenic substrate of peroxidase. Peroxidase generates O2 from H2O2 produced by the lactobacilli, and the TMB stains the colonies blue in the presence of O2. Thus, after 48 hours of incubation under 5% CO2 in air, the colonies that produce H2O2 on MRS agar appear dark blue. H2O2 nonproducers are colorless. It has been used to study the stabilization effect of polyvinyl alcohol on horseradish peroxidase. It is also used for the determination of glucose and peroxides in solution.
Biochem/physiol Actions
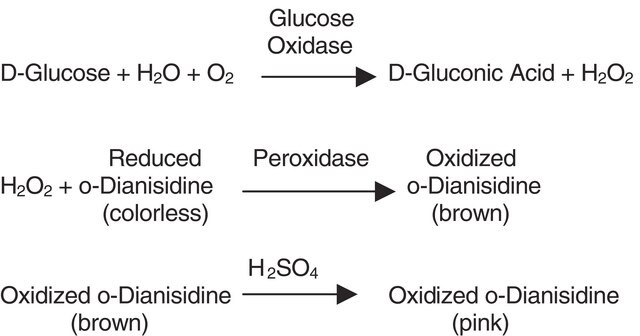
HRP readily combines with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and the resultant [HRP-H2O2] complex can oxidize a wide variety of hydrogen donors. The optimal pH is 6.0-6.5 and the enzyme is most stable in the pH range of 5.0-9.0. HRP can be conjugated to antibodies by several different methods that include the use of glutaraldehyde, periodate oxidation, disulfide bonds, and also via amino and thiol directed cross-linkers. It is smaller and more stable than the enzyme labels, β-galactosidase and alkaline phosphatase. Hence, it is the most desired label. Also, its glycosylation leads to lower non-specific binding. Sodium azide, cyanide, L-cystine, dichromate, ethylenethiourea, hydroxylamine, sulfide, vanadate, p-aminobenzoic acid, as well as Cd2+, Co2+, Cu2+, Fe3+, Mn2+, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions are found to inhibit the enzyme activity.
When incubated with a substrate, horseradish peroxidase produces a coloured, fluorimetric, or luminescent derivative of the labeled molecule, allowing quantification. Horseradish peroxidase has been shown to slightly reduce the level of inhibition in a cydAB mutant.
Packaging
Packaged in mg solid
Unit Definition
One ABTS unit will oxidize 1 μmole of ABTS per minute at 25 °C at pH 5.0
One pyrogallol unit will form 1.0 mg purpurogallin from pyrogallol in 20 sec at pH 6.0 at 20 °C.
Preparation Note
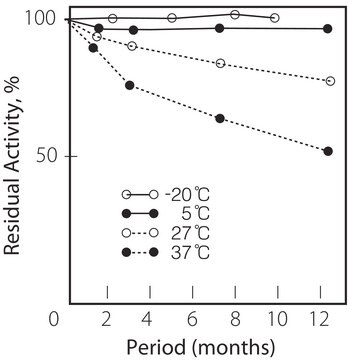
Solutions of this product at 1 mg/mL in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 6.0) remain active for at least two weeks at room temperature. The solution retains activity after 5 freeze-thaw cycles.
Analysis Note
The RZ (Reinheitszahl) is the absorbance ratio A403/A275 determined at 0.5-1.0 mg/ml in deionized water. It is a measure of hemin content, not enzymatic activity. Even preparations with high RZ may have low enzymatic activity.
This product is assayed using ABTS for easy comparison to other suppliers′ unit: approx. 1,000 units per mg solid