推薦產品
一般說明
研究领域:细胞信号转导
胆固醇酯酶(CE)是一种糖蛋白,可从柱状假丝酵母和荧光假单胞菌等真菌中提取。属于脂肪酶/酯酶家族成员,以同型二聚体形式发挥作用。胆固醇酯酶在胰腺中生成,经胆囊收缩素(CCK)刺激后以活性形式释放。
胆固醇酯酶(CE)是一种糖蛋白,可从柱状假丝酵母和荧光假单胞菌等真菌中提取。属于脂肪酶/酯酶家族成员,以同型二聚体形式发挥作用。胆固醇酯酶在胰腺中生成,经胆囊收缩素(CCK)刺激后以活性形式释放。
應用
胆固醇酯酶(来自荧光假单胞菌)用于:
- 在胆固醇酯酶检测中用于定量分析人血清样本中的总胆固醇
- 脂解制备物酯酶活性的非变性蛋白电转移研究
- 酶法胆固醇测定试剂(含胆固醇氧化酶)的组分优化研究
- 修饰人血浆低密度脂蛋白(LDL),用于在分支组织工程血管(TEBV)中诱导内皮细胞(EC)障碍和单核细胞黏附(MC)
- 在菲律宾菌素染色法检测视网膜冷冻切片CE中,水解天然胆固醇酯(CE)
该酶广泛应用于诊断实验室血清胆固醇的测定。
生化/生理作用
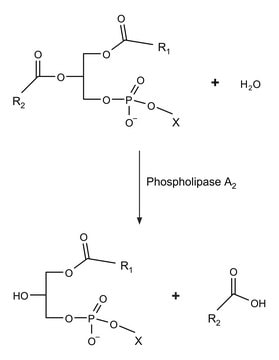
胆固醇酯酶(CE)是一种可水解或合成胆固醇等固醇物质脂肪酸酯部分的可逆性酶。胆固醇酯酶活性在类固醇生物合成或类固醇从头合成(de novo steroidogenesis)中起重要作用。对水不溶性长链脂肪酸酯的水解需要胆汁盐激活。对水溶性短链脂肪酸酯和溶血磷脂的水解则不需要胆汁盐激活。还可水解甘油三酯、甘油二酯和甘油一酯、磷脂、溶血磷脂和神经酰胺。该酶在脂质和脂蛋白代谢以及动脉粥样硬化中起多种作用。
其他說明
含有磷酸钾和 TRITON®X-100。
單位定義
在牛磺胆酸盐存在下,一个单位在 pH7.0,37°C 下每分钟将 1.0μ 摩尔胆固醇油酸酯水解成胆固醇和油酸。
分析報告
双缩脲法测定蛋白质。
訊號詞
Danger
危險聲明
危險分類
Resp. Sens. 1
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
分析證明 (COA)
輸入產品批次/批號來搜索 分析證明 (COA)。在產品’s標籤上找到批次和批號,寫有 ‘Lot’或‘Batch’.。
客戶也查看了
Jounghyun H Lee et al.
Advanced biology, 5(4), e2000428-e2000428 (2021-04-15)
Atherosclerosis begins with the accumulation of cholesterol-carrying lipoproteins on blood vessel walls and progresses to endothelial cell dysfunction, monocyte adhesion, and foam cell formation. Endothelialized tissue-engineered blood vessels (TEBVs) have previously been fabricated to recapitulate artery functionalities, including vasoconstriction, vasodilation
Carolina Espinosa Álvarez et al.
Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 25(24) (2020-12-30)
Haematococcus pluvialis is the largest producer of natural astaxanthin in the world. Astaxanthin is a bioactive compound used in food, feed, nutraceutics, and cosmetics. In this study, astaxanthin extraction from H. pluvialis by supercritical fluid extraction was evaluated. The effects
David Y Hui et al.
Journal of lipid research, 43(12), 2017-2030 (2002-11-28)
Carboxyl ester lipase (CEL), previously named cholesterol esterase or bile salt-stimulated (or dependent) lipase, is a lipolytic enzyme capable of hydrolyzing cholesteryl esters, tri-, di-, and mono-acylglycerols, phospholipids, lysophospholipids, and ceramide. The active site catalytic triad of serine-histidine-aspartate is centrally
Peter E Thelwall et al.
Journal of hepatology, 59(3), 543-549 (2013-04-30)
Lysosomal Acid Lipase (LAL) deficiency is a rare metabolic storage disease, caused by a marked reduction in activity of LAL, which leads to accumulation of cholesteryl esters (CE) and triglycerides (TG) in lysosomes in many tissues. We used (1)H magnetic
Stuart A Scott et al.
Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.), 58(3), 958-965 (2013-02-21)
Cholesteryl ester storage disease (CESD) and Wolman disease are autosomal recessive later-onset and severe infantile disorders, respectively, which result from the deficient activity of lysosomal acid lipase (LAL). LAL is encoded by LIPA (10q23.31) and the most common mutation associated
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務