About This Item
推薦產品
生物源
Zygosporium mansonii
品質等級
化驗
≥98% (TLC and HPLC)
形狀
powder
溶解度
DMSO: soluble
ethanol: soluble
抗生素活性譜
fungi
作用方式
DNA synthesis | interferes
儲存溫度
−20°C
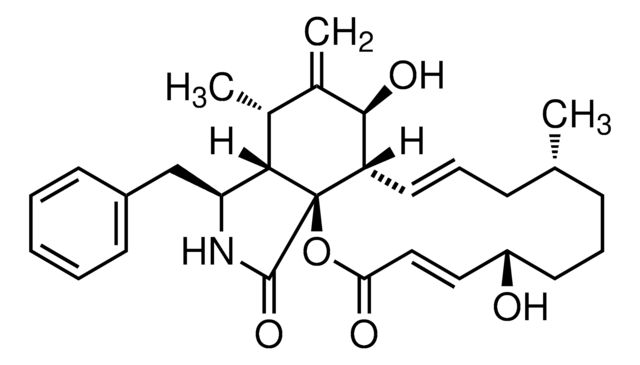
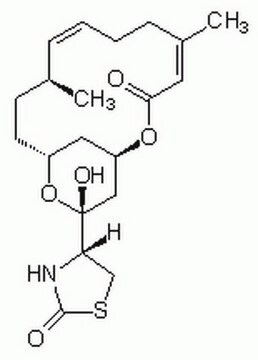
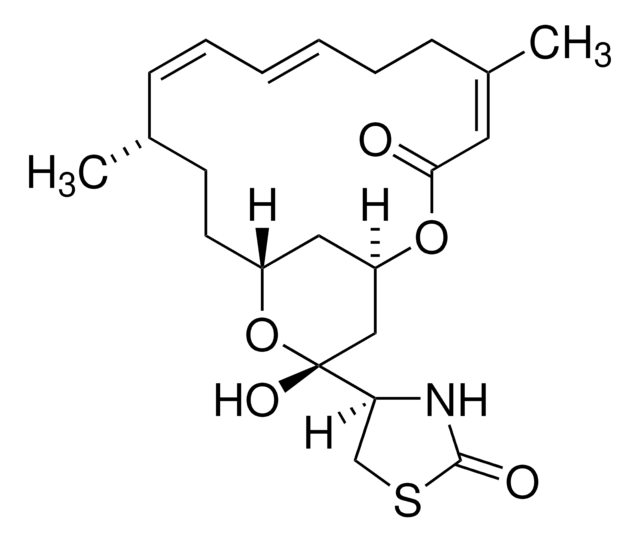
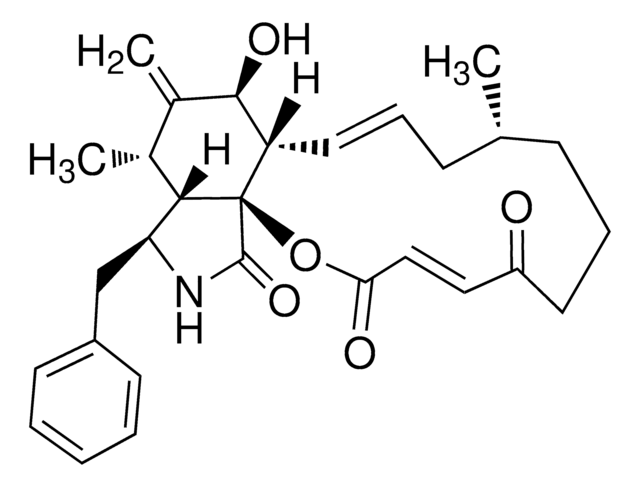
SMILES 字串
[H][C@@]12[C@H](C)C(=C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]3\C=C\C[C@H](C)C(=O)[C@](C)(O)\C=C\[C@@H](OC(C)=O)[C@@]13C(=O)N[C@H]2Cc4ccccc4
InChI
1S/C30H37NO6/c1-17-10-9-13-22-26(33)19(3)18(2)25-23(16-21-11-7-6-8-12-21)31-28(35)30(22,25)24(37-20(4)32)14-15-29(5,36)27(17)34/h6-9,11-15,17-18,22-26,33,36H,3,10,16H2,1-2,4-5H3,(H,31,35)/b13-9+,15-14+/t17-,18+,22-,23-,24+,25-,26+,29+,30+/m0/s1
InChI 密鑰
SDZRWUKZFQQKKV-JHADDHBZSA-N
尋找類似的產品? 前往 產品比較指南
一般說明
應用
- 处理H9c2 细胞以研究细胞刚度和F-肌动蛋白细胞骨架的关系
- 作为受体介导的内吞作用的抑制剂用于处理少突胶质前体细胞 (OPCs),以研究其抑制特异性细胞外囊泡(EV) 摄取途径的作用
- 在体外胚胎培养中用于人工激活卵母细胞
生化/生理作用
訊號詞
Danger
危險聲明
危險分類
Acute Tox. 2 Oral
儲存類別代碼
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
分析證明 (COA)
輸入產品批次/批號來搜索 分析證明 (COA)。在產品’s標籤上找到批次和批號,寫有 ‘Lot’或‘Batch’.。
客戶也查看了
文章
High titer lentiviral particles including beta-actin, alpha-tubulin and vimentin used for live cell analysis of cytoskeleton structure proteins.
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務