推薦產品
product name
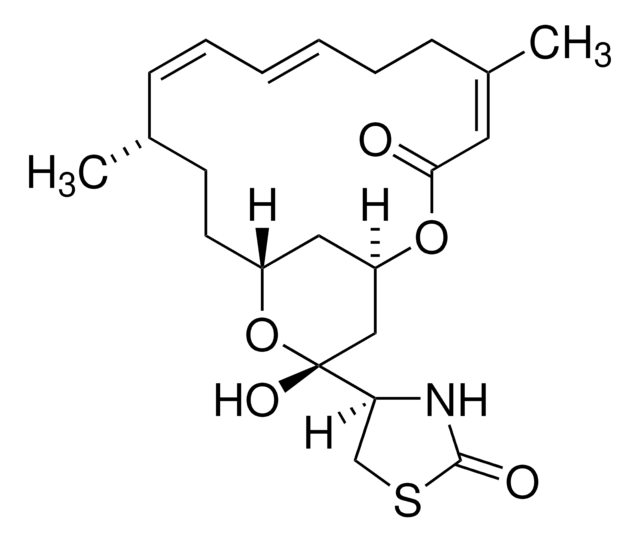
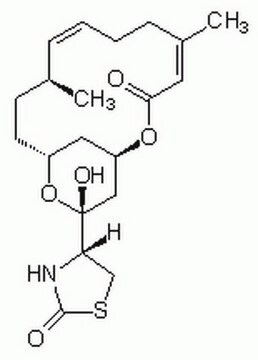
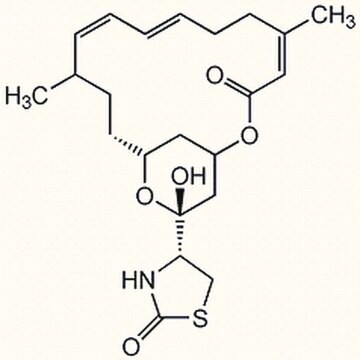
红海海绵素A,来源于Latrunculia magnifica, Latrunculin A, CAS 76343-93-6, is a cell-permeable marine toxin that disrupts microfilament organization in cultured cells by the formation of a 1:1 complex with monomeric G-actin (KD = 200 nM).
品質等級
化驗
≥95% (HPLC)
形狀
solid
製造商/商標名
Calbiochem®
儲存條件
OK to freeze
protect from light
顏色
white
溶解度
DMSO: 25 mg/mL
運輸包裝
ambient
儲存溫度
−20°C
InChI
1S/C22H31NO5S/c1-15-7-5-3-4-6-8-16(2)11-20(24)27-18-12-17(10-9-15)28-22(26,13-18)19-14-29-21(25)23-19/h3-5,7,11,15,17-19,26H,6,8-10,12-14H2,1-2H3,(H,23,25)/b4-3+,7-5-,16-11-/t15-,17-,18-,19+,22-/m1/s1
InChI 密鑰
DDVBPZROPPMBLW-IZGXTMSKSA-N
一般說明
一种可渗透细胞的海洋毒素,通过与单体G-肌动蛋白(Kd=200 nM)形成1:1的复合物来破坏培养细胞中的微丝组织。也是精子,卵子和胚胎中微丝介导过程的有效抑制剂。1 mM(50 µg/119µ l)的Latrunculin A,Latrunculia magnifica目录号 428026的DMSO溶液也可用。
来自红海海绵Latrunculia magnifica的可渗透细胞的海洋毒素,通过与单体G-肌动蛋白(Kd=200 nM)形成1:1的复合物来破坏培养细胞中的微丝组织。也是精子,卵子和胚胎中微丝介导过程的有效抑制剂。
生化/生理作用
与单体G-肌动蛋白形成1:1复合物中Kd=200 nM
主要靶标
G-肌动蛋白
G-肌动蛋白
产物不与ATP竞争。
可逆:否
细胞可渗透性:具有
包裝
用惰性气体包装
警告
毒性:有害(C)
重構
复溶后等分并冷冻保存(-20°C)。贮备液在-20°C下可稳定保存至多3个月。
其他說明
Ayscough, K.R., et al. 1997.J. Cell Biol. 137, 399.
Spector, I., et al. 1989.Cell Motil.Cytoskeleton 13, 127.
Coue, M., et al. 1987.FEBS Lett.213, 316.
Schatten, G., et al. 1986.Exp.Cell Res. 166, 191.
Spector, I., et al. 1983.Science 219, 493.
Spector, I., et al. 1989.Cell Motil.Cytoskeleton 13, 127.
Coue, M., et al. 1987.FEBS Lett.213, 316.
Schatten, G., et al. 1986.Exp.Cell Res. 166, 191.
Spector, I., et al. 1983.Science 219, 493.
法律資訊
CALBIOCHEM is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
分析證明 (COA)
輸入產品批次/批號來搜索 分析證明 (COA)。在產品’s標籤上找到批次和批號,寫有 ‘Lot’或‘Batch’.。
客戶也查看了
Ao Liu et al.
Molecular biology of the cell, 32(20), ar5-ar5 (2021-08-05)
Mitochondrial division is an important cellular process in both normal and pathological conditions. The dynamin GTPase Drp1 is a central mitochondrial division protein, driving constriction of the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM). In mammals, the OMM protein mitochondrial fission factor (Mff)
Rong Liu et al.
Cell reports, 37(11), 110110-110110 (2021-12-16)
Mechanisms driving the prolonged meiotic prophase I in mammals are poorly understood. RNA helicase YTHDC2 is critical for mitosis to meiosis transition. However, YTHDC2 is highly expressed in pachytene cells. Here we identify an essential role for YTHDC2 in meiotic
Xin Wei et al.
Journal of virology, 94(17) (2020-06-12)
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS), caused by PRRS virus (PRRSV), has led to enormous economic losses in global swine industry. Infection by PRRSV is previously shown to be via low pH-dependent clathrin-mediated endocytosis, and CD163 functions as an essential
George R R Bell et al.
Nature communications, 12(1), 6148-6148 (2021-11-18)
During chemotaxis, neutrophils use cell surface G Protein Coupled Receptors to detect chemoattractant gradients. The downstream signaling system is wired with multiple feedback loops that amplify weak inputs and promote spatial separation of cell front and rear activities. Positive feedback could
Reem Abu Rass et al.
Frontiers in cell and developmental biology, 10, 1075364-1075364 (2023-01-07)
Tilapia Lake Virus (TiLV) is an emerging virus lethal to tilapia, which threatens the global tilapia aquaculture with severe implications for food security. TiLV possesses similar features to orthomyxoviruses but is classified in the sole and the monotypic genus Tilapinevirus
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務