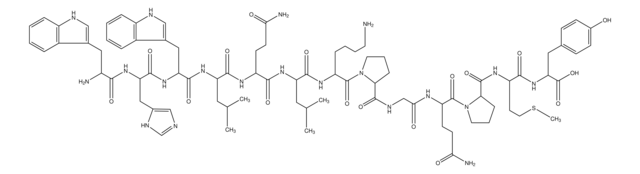
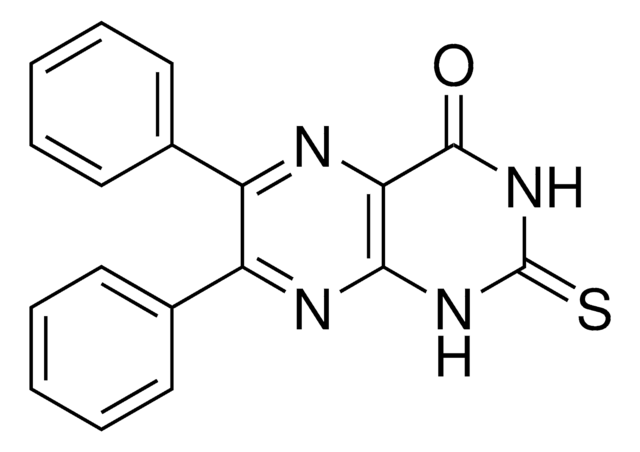
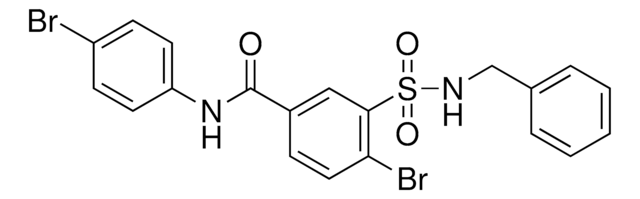
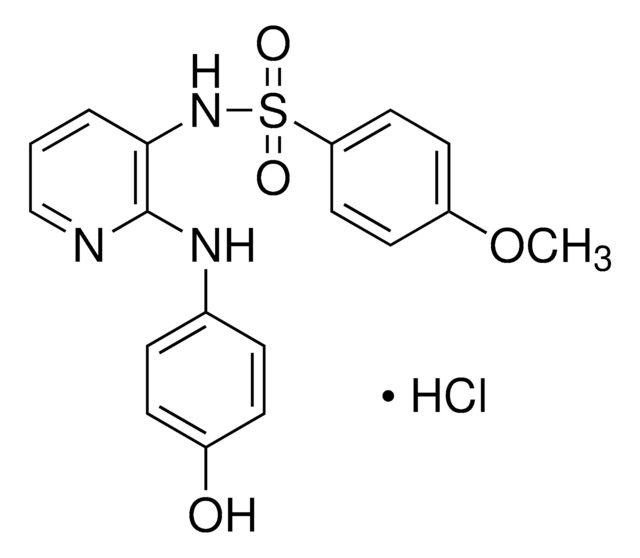
推薦產品
品質等級
化驗
≥99% (TLC)
形狀
powder
mp
300 °C (dec.)
溶解度
DMSO: soluble 10 mg/mL (may require heating)
H2O: insoluble
儲存溫度
2-8°C
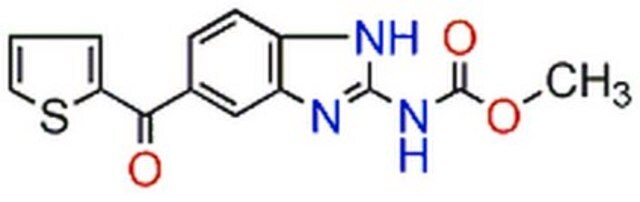
SMILES 字串
COC(=O)Nc1nc2cc(ccc2[nH]1)C(=O)c3cccs3
InChI
1S/C14H11N3O3S/c1-20-14(19)17-13-15-9-5-4-8(7-10(9)16-13)12(18)11-3-2-6-21-11/h2-7H,1H3,(H2,15,16,17,19)
InChI 密鑰
KYRVNWMVYQXFEU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
基因資訊
human ... TUBB(203068)
尋找類似的產品? 前往 產品比較指南
一般說明
應用
生化/生理作用
外觀
訊號詞
Warning
危險聲明
危險分類
Muta. 2 - Repr. 2
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
客戶也查看了
文章
The CRISPR-Cas9 system is an RNA-guided genome-editing tool that provides researchers a simple, easy, and quick way to modify the genomes of various organisms.
High titer lentiviral particles including beta-actin, alpha-tubulin and vimentin used for live cell analysis of cytoskeleton structure proteins.
我們的科學家團隊在所有研究領域都有豐富的經驗,包括生命科學、材料科學、化學合成、色譜、分析等.
聯絡技術服務