推荐产品
生物源
rabbit
品質等級
共軛
unconjugated
抗體表格
affinity isolated antibody
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
polyclonal
形狀
buffered aqueous solution
分子量
~48 kDa
物種活性
rat, mouse, human
濃度
~1 mg/mL
技術
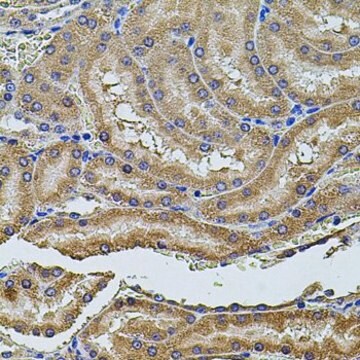
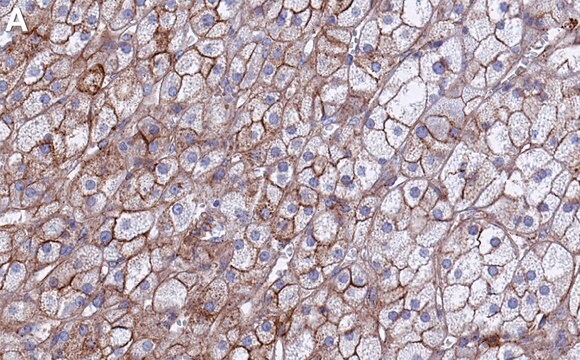
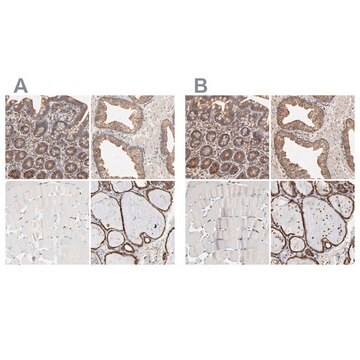
indirect immunofluorescence: 5-10 μg/mL using human HEK-293K cells
western blot: 0.5-1 μg/mL using whole extract of mouse lung
western blot: 1-2 μg/mL using whole extract of rat lung
UniProt登錄號
運輸包裝
dry ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
基因資訊
human ... FLOT1(10211)
mouse ... Flot1(14251)
rat ... Flot1(64665)
一般說明
Flotillin 1(FLOT1)也称为reggie-2,是一种雌激素反应性基因,位于人类染色体6p21.33。该基因编码整合膜蛋白和脂筏的成分。
Flotillin 是脂筏(lipid raft)相关蛋白,主要在脂肪组织、条纹肌肉组织和肺中表达。 它在多种细胞过程(如吞噬、胞吞、胰岛素信号传导和神经元再生)中起关键作用。抗flotillin 1 抗体可用于免疫印迹和免疫定位。兔抗flotillin 1抗体与大鼠、小鼠和人的flotillin 1 发生特异反应。
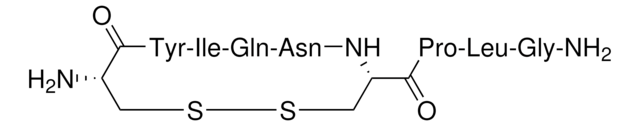
免疫原
对应于小鼠脂筏标记蛋白 1 的氨基酸残基 413-428 的合成肽,N-端添加了半胱氨酸,与 KLH 偶联。与大鼠中的相应序列相同,与人的相应序列相差 1 个氨基酸。
應用
兔抗-脂筏标记蛋白 1 抗体可用于免疫印迹分析。
抗脂筏标记蛋白 1 抗体可用于免疫荧光和蛋白质印迹。
生化/生理作用
Flotillin 1((FLOT1)在胞吞作用中起一定作用。它也在生长因子信号传导中起作用,并激活丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号传导。此外,它还参与吞噬作用以及肌动蛋白细胞骨架和膜转运的调节。该蛋白还与肿瘤进展有关,在许多癌症(包括乳腺癌)中表达。
標靶描述
脂筏标记蛋白 1 编码与小窝相关的完整膜蛋白。小窝是内在细胞膜上的小区域,参与囊泡运输和信号转导。
外觀
0.01M 磷酸缓冲盐溶液,pH 7.4,含 15mM 叠氮化钠。
免責聲明
除非我们的产品目录或产品附带的其他公司文档另有说明,否则我们的产品仅供研究使用,不得用于任何其他目的,包括但不限于未经授权的商业用途、体外诊断用途、离体或体内治疗用途或任何类型的消费或应用于人类或动物。
未找到合适的产品?
试试我们的产品选型工具.
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Gloves, multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US)
Takeshi Yamasaki et al.
The Journal of general virology, 93(Pt 3), 668-680 (2011-11-18)
Generation of an abnormal isoform of the prion protein (PrP(Sc)) is a key aspect of the propagation of prions. Elucidation of the intracellular localization of PrP(Sc) in prion-infected cells facilitates the understanding of the cellular mechanism of prion propagation. However
Carsten Frühbeis et al.
Journal of extracellular vesicles, 4, 28239-28239 (2015-07-05)
Cells secrete extracellular vesicles (EVs) by default and in response to diverse stimuli for the purpose of cell communication and tissue homeostasis. EVs are present in all body fluids including peripheral blood, and their appearance correlates with specific physiological and
Rajesh Khanna et al.
Pain, 160(7), 1644-1661 (2019-04-02)
Inhibition of voltage-gated calcium (CaV) channels is a potential therapy for many neurological diseases including chronic pain. Neuronal CaV1/CaV2 channels are composed of α, β, γ and α2δ subunits. The β subunits of CaV channels are cytoplasmic proteins that increase
Brett Nixon et al.
Journal of cellular physiology, 226(10), 2651-2665 (2011-07-28)
Mammalian spermatozoa attain the ability to fertilize an oocyte as they negotiate the female reproductive tract. This acquisition of functional competence is preceded by an intricate cascade of biochemical and functional changes collectively known as "capacitation." Among the universal correlates
Anastasia Chillà et al.
Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP, 12(7), 1926-1938 (2013-04-11)
Endothelial cell caveolar-rafts are considered functional platforms that recruit several pro-angiogenic molecules to realize an efficient angiogenic program. Here we studied the differential caveolar-raft protein composition of endothelial colony-forming cells following stimulation with VEGF, which localizes in caveolae on interaction
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门