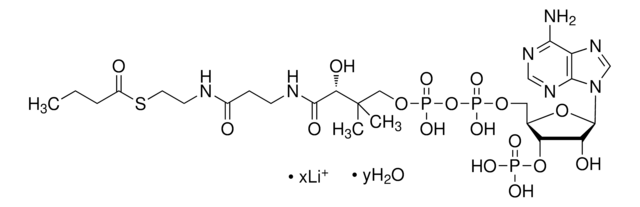
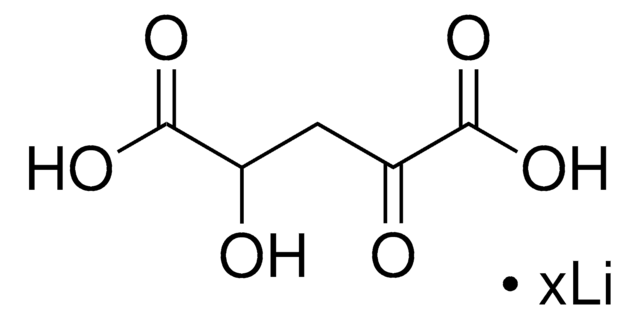
C3260
Citrate Synthase from porcine heart
ammonium sulfate suspension, ≥100 units/mg protein
Synonym(s):
Citrate condensing enzyme, Citrate oxaloacetate lyase (CoA-acetylating)
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
CAS Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.54
Recommended Products
biological source
Porcine heart
Quality Level
form
ammonium sulfate suspension
specific activity
≥100 units/mg protein
mol wt
98 kDa ( 49 kDa monomer)
solubility
H2O: soluble 1.0 mg/mL, clear
foreign activity
isocitrate dehydrogenase and aconitase ≤0.01%
malic dehydrogenase ≤0.1%
storage temp.
2-8°C
Application
Citrate Synthase from porcine heart has been used:
- to inject newt egg for determining its importance in egg activation at fertilization
- in the preparation of reaction mix to determine pyruvate carboxylase enzyme activity
- to examine whether it can induce a [Ca2+] increase and egg activation in unfertilized eggs
Biochem/physiol Actions
Citrate synthase catalyses the conversion of citrate to acetyl-CoA in the presence of coenzyme-A with the release of H2O and oxaloacetate. The enzyme has a molecular weight of 85 kDa and a pI of 6.1-6.6. It is inhibited by fluoroacetyl-CoA, palmitoyl-CoA, and citroyl-CoA. It is also inhibited when it is acetylated by acetic anhydride or iodinated by iodine.
Unit Definition
One unit will form 1.0 μmole of citrate from oxalacetate and acetyl CoA per min at pH 8.0 at 37 °C.
Physical form
Suspension in 3.2 M (NH4)2SO4 solution, pH 7.0.
Preparation Note
Dissolves in water to form a clear solution at 1 mg/mL concentration.
Storage Class
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Florian Stengel et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(5), 2007-2012 (2010-02-06)
Small Heat Shock Proteins (sHSPs) are a diverse family of molecular chaperones that prevent protein aggregation by binding clients destabilized during cellular stress. Here we probe the architecture and dynamics of complexes formed between an oligomeric sHSP and client by
Oded Rimon et al.
Antioxidants & redox signaling, 27(15), 1252-1267 (2017-04-11)
A recently discovered group of conditionally disordered chaperones share a very unique feature; they need to lose structure to become active as chaperones. This activation mechanism makes these chaperones particularly suited to respond to protein-unfolding stress conditions, such as oxidative
Xiangjian Gou et al.
Plant biotechnology journal, 20(7), 1417-1431 (2022-04-11)
Single amino acid substitution (SAAS) produces the most common variant of protein function change under physiological conditions. As the number of SAAS events in plants has increased exponentially, an effective prediction tool is required to help identify and distinguish functional
Skylar Xantus Kim et al.
eLife, 7 (2018-07-17)
Anhydrobiotes are rare microbes, plants and animals that tolerate severe water loss. Understanding the molecular basis for their desiccation tolerance may provide novel insights into stress biology and critical tools for engineering drought-tolerant crops. Using the anhydrobiote, budding yeast, we
Alterations in Cytosolic and Mitochondrial [U-13C] Glucose Metabolism in a Chronic Epilepsy Mouse Model
McDonald TS, et al.
eNeuro, 4(1), 266-276 (2017)
Articles
Instructions for working with enzymes supplied as ammonium sulfate suspensions
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service