16682
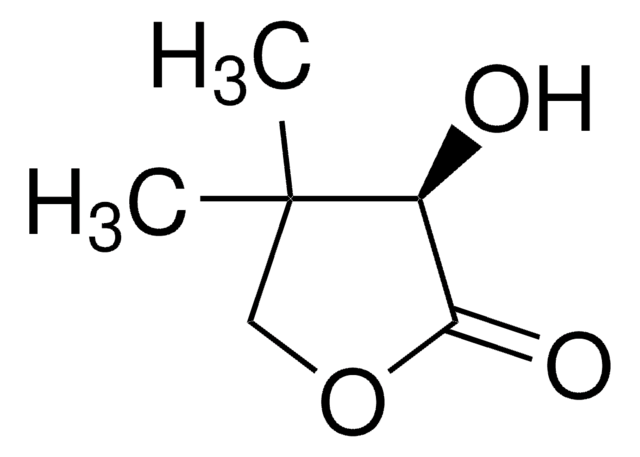
(R)-Pantoic acid sodium salt
≥95% (GC)
Synonym(s):
(2R)-2,4-Dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanoic acid monosodium salt, (R)-2,4-Dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutyric acid sodium salt, Sodium (R)-pantoate, Sodium D-pantoate
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C6H11NaO4
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
170.14
Beilstein/REAXYS Number:
6119584
UNSPSC Code:
12352106
NACRES:
NA.25
Recommended Products
Quality Level
assay
≥95% (GC)
optical activity
[α]/D 8.0±1.0°, c = 1 in H2O
storage temp.
−20°C
InChI
1S/C6H12O4.Na/c1-6(2,3-7)4(8)5(9)10;/h4,7-8H,3H2,1-2H3,(H,9,10);/q;+1/p-1/t4-;/m0./s1
InChI key
XTIMSSMEPPKSQD-WCCKRBBISA-M
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Biochem/physiol Actions
(R)-Pantoic acid is an intermediate in the phosphopantothenate biosynthesis pathway for the de novo synthesis of R-pantothenate (vitamin B5) from valine in plants and microorganisms.
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
13C-NMR and 1H-1H NOEs of Coenzyme A: conformation of the pantoic acid moiety.
Dordine, R.L., et al.
Bioorganic Chemistry, 23, 169-181 (1995)
Analysis of stereochemistry of enzymically formed pantoyl lactone or pantoic acid by gas chromatography and circular dichroism.
D R Wilken et al.
Analytical biochemistry, 112(1), 9-16 (1981-03-15)
Hiroya Tomita et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 194(19), 5434-5443 (2012-08-07)
Although bacteria and eukaryotes share a pathway for coenzyme A (CoA) biosynthesis, we previously clarified that most archaea utilize a distinct pathway for the conversion of pantoate to 4'-phosphopantothenate. Whereas bacteria/eukaryotes use pantothenate synthetase and pantothenate kinase (PanK), the hyperthermophilic
Michael Rothmann et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 135(16), 5962-5965 (2013-04-05)
Pantetheine and its corresponding disulfide pantethine play a key role in metabolism as building blocks of coenzyme A (CoA), an essential cofactor utilized in ~4% of primary metabolism and central to fatty acid, polyketide, and nonribosomal peptide synthases. Using a
Dayong Si et al.
Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 93(4), 1619-1625 (2011-11-16)
Ketopantoic acid (KPA) reductase catalyzes the stereospecific reduction of ketopantoic acid to D-pantoic acid. Based on the N-terminal amino acid sequence of KPA reductase from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia 845, the KPA reductase gene was cloned from S. maltophilia NBRC14161 and sequenced.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service