NA29
Anti-p16 (Ab-1) Mouse mAb (DCS-50.1/H4)
liquid, clone DCS-50.1/H4, Calbiochem®
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352203
NACRES:
NA.43
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
antibody form
purified antibody
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
DCS-50.1/H4, monoclonal
form
liquid
contains
≤0.1% sodium azide as preservative
species reactivity
human
manufacturer/tradename
Calbiochem®
storage condition
do not freeze
isotype
IgG1
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
2-8°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
General description
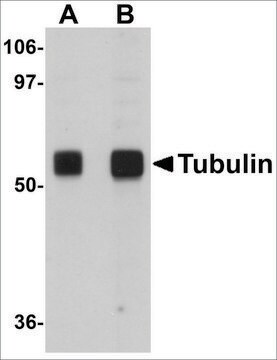
Purified mouse monoclonal antibody generated by immunizing BALB/c mice with the specified immunogen and fusing splenocytes with NS-2 mouse myeloma cells. Recognizes the ~16 kDa p16 protein.
Recognizes the ~16 kDa p16 protein in Saos-2 cells and bladder tissue. Sold under license of U.S. Patent 6,482,929. Sold under license of U.S. Patent 5,843,756, 6,090,578, and corresponding patents.
This Anti-p16 (Ab-1) Mouse mAb (DCS-50.1/H4) is validated for use in Immunoblotting for the detection of p16 (Ab-1).
Immunogen
Human
recombinant, human p16
Application
Immunoblotting (0.5-5 µg/ml, see application references)
Packaging
Please refer to vial label for lot-specific concentration.
Warning
Toxicity: Standard Handling (A)
Physical form
In 0.05 M sodium phosphate buffer, 0.2% gelatin pH 7.5.
Analysis Note
Negative Control
U2OS cells
U2OS cells
Positive Control
Saos-2 cells or bladder tissue
Saos-2 cells or bladder tissue
Other Notes
Does not cross-react with the closely related p15 protein. Antibody should be titrated for optimal results in individual systems.
Koh, J., et al. 1995. Nature375, 506.
Lukas, J., et al. 1995. Nature375, 503.
Cheng, J.Q., et al. 1994. Cancer Res.54, 5547.
Jen, J., et al. 1994. Cancer Res.54, 6353.
Kamb, A., et al. 1994 Science264, 436.
Nobori, T., Miura, K., et al. 1994. Nature368, 753.
Okamoto, A., Demetrick, D.J., et al. 1994. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA91, 11045.
Serrano, M., et al. 1993. Nature366 704.
Lukas, J., et al. 1995. Nature375, 503.
Cheng, J.Q., et al. 1994. Cancer Res.54, 5547.
Jen, J., et al. 1994. Cancer Res.54, 6353.
Kamb, A., et al. 1994 Science264, 436.
Nobori, T., Miura, K., et al. 1994. Nature368, 753.
Okamoto, A., Demetrick, D.J., et al. 1994. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA91, 11045.
Serrano, M., et al. 1993. Nature366 704.
Legal Information
Sold under license of U.S. Patents 5,843,756, 6,090,578 and corresponding patents.
CALBIOCHEM is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
wgk_germany
nwg
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Noriyasu Usami et al.
Oncogene, 22(39), 7923-7930 (2003-09-13)
We have found that a malignant mesothelioma cell line, NCI-H28, had a chromosome 3p21.3 homozygous deletion containing the beta-catenin gene (CTNNB1), which suggested that the deletion of beta-catenin might have a growth advantage in the development of this tumor. To
Goro Sashida et al.
Molecular and cellular biology, 29(13), 3687-3699 (2009-04-22)
Several ETS transcription factors, including ELF4/MEF, can function as oncogenes in murine cancer models and are overexpressed in human cancer. We found that Elf4/Mef activates Mdm2 expression; thus, lack of or knockdown of Elf4/Mef reduces Mdm2 levels in mouse embryonic
J L Nargi et al.
Neoplasia (New York, N.Y.), 1(6), 544-556 (2000-08-10)
Epidemiological evidence has suggested an association between diets rich in antioxidants and diminished risks of various types of cancer. Proposed mechanisms for protective effects of antioxidants have involved inhibition of free radical-mediated DNA damage. Recent data suggest that antioxidants may
Masashi Narita et al.
Cell, 113(6), 703-716 (2003-06-18)
Cellular senescence is an extremely stable form of cell cycle arrest that limits the proliferation of damaged cells and may act as a natural barrier to cancer progression. In this study, we describe a distinct heterochromatic structure that accumulates in
Alessandro Bertolo et al.
Scientific reports, 10(1), 19084-19084 (2020-11-07)
Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC) are used in cell therapy, but results depend on the unknown quality of cell populations. Extended culture time of MSC increases their senescent levels, leading to a critical loss of cell fitness. Here, we tested the
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service