MABN323
Anti-Ermin Antibody, clone 160
clone 160, from mouse
Synonym(s):
Ermin, Juxtanodin
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
160, monoclonal
species reactivity
mouse, rat
technique(s)
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunohistochemistry: suitable
western blot: suitable
isotype
IgG2aκ
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
wet ice
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
mouse ... Ermn(77767)
General description
Immunogen
Application
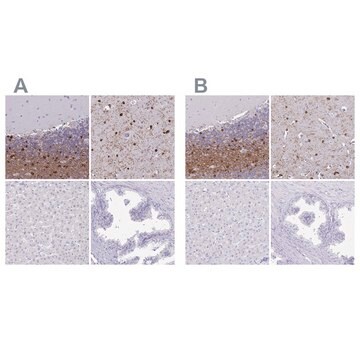
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A representative lot from an independent laboratory detected Ermin in certain mouse brain and optic nerve sections (Brockschnieder, D., et al. (2006). J Neurosci. 26(3):737-762).
Neuroscience
Developmental Neuroscience
Quality
Western Blotting Analysis: 1 µg/mL of this antibody detected Ermin in 10 µg of mouse brain tissue lysate.
Target description
Physical form
Storage and Stability
Analysis Note
Mouse brain tissue lysate
Other Notes
Disclaimer
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service