SRP0120
Sirtuin 6 human
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, ≥70% (SDS-PAGE)
Synonim(y):
NAD-dependent ADP-ribosyltransferase sirtuin-6, SIR2L6, SIRT6, sir2-like 6
Zaloguj sięWyświetlanie cen organizacyjnych i kontraktowych
About This Item
Kod UNSPSC:
12352200
NACRES:
NA.32
Polecane produkty
pochodzenie biologiczne
human
rekombinowane
expressed in E. coli
Próba
≥70% (SDS-PAGE)
Formularz
aqueous solution
masa cząsteczkowa
65 kDa
opakowanie
pkg of 100 μg
warunki przechowywania
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
stężenie
>0.02 mg/mL
numer dostępu NCBI
numer dostępu UniProt
Warunki transportu
dry ice
temp. przechowywania
−70°C
informacje o genach
human ... SIRT6(51548)
Opis ogólny
Sirtuina 6 (Sir6) jest kodowana przez gen zmapowany na ludzkim chromosomie 19p13.3, regionie związanym z rozwojem ostrej białaczki. Sir 6 ulega ekspresji głównie w komórkach kostnych i jajnikach, ale nie występuje w szpiku kostnym. Sirt6 jest białkiem związanym z chromatyną, zlokalizowanym specyficznie w jądrze.
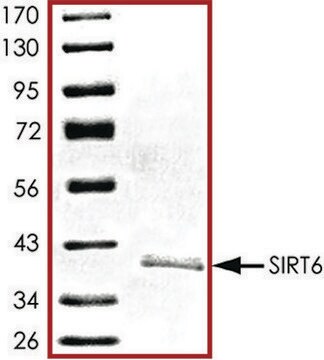
Ludzka Sirtuina 6, GenBank Accession No. NM_016539), pełnej długości z N-końcowym znacznikiem ST, MW = 65kDa, wyrażana w systemie ekspresji Escherichia coli.
Ludzka Sirtuina 6, GenBank Accession No. NM_016539), pełnej długości z N-końcowym znacznikiem ST, MW = 65kDa, wyrażana w systemie ekspresji Escherichia coli.
Zastosowanie
Useful for the study of enzyme kinetics, screening inhibitors, and selectivity profiling.
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Sirtuina 6 (Sir6) jest mono-ADP-rybozylotransferazą, która katalizuje transfer cząsteczki ADP-rybozy z NAD do siebie i histonów. Jest ona zaangażowana w regulację naprawy DNA, stabilności genomu i integralności telomerów, ekspresji genów i metabolizmu. Ponadto zapobiega zaburzeniom związanym z wiekiem i przedwczesnemu starzeniu się. Sir6 odgrywa istotną rolę w hamowaniu odpowiedzi zapalnych w stawach reumatoidalnych, w których pośredniczy czynnik jądrowy NF-κB. Dlatego też Sir6 jest uważany za silny cel w leczeniu reumatoidalnego zapalenia stawów (RZS). Sir6 jest również zaangażowany w regulację metabolizmu glukozy i tłuszczów. Sir6 zapobiega przerostowi mięśnia sercowego in vitro poprzez hamowanie aktywności transkrypcyjnej zależnej od NF-κB, a efekt ten opiera się na jego aktywności deacetylazy.
Postać fizyczna
Formuła w 25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8,0, 100 mM NaCl, 0,05% Tween-20 i 20% glicerolu.
Uwaga dotycząca przygotowania
Thaw on ice. Upon first thaw, briefly spin tube containing enzyme to recover full content of the tube. Aliquot enzyme into single use aliquots. Store remaining undiluted enzyme in aliquots at -70°C. Note: Enzyme is very sensitive to freeze/thaw cycles.
Ta strona może zawierać tekst przetłumaczony maszynowo.
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Lot/Batch Number
Nie widzisz odpowiedniej wersji?
Jeśli potrzebujesz konkretnej wersji, możesz wyszukać konkretny certyfikat według numeru partii lub serii.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Abhishek Bhardwaj et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113(5), E538-E547 (2016-01-21)
SIRT6 (sirtuin 6) is a member of sirtuin family of deacetylases involved in diverse processes including genome stability, metabolic homeostasis, and tumorigenesis. However, the role of SIRT6 deacetylase activity in its tumor-suppressor functions is not well understood. Here we report
Neural sirtuin 6 (Sirt6) ablation attenuates somatic growth and causes obesity.
Schwer B
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 107(50), 21790-21794 (2010)
Chromosomal organization and fluorescence in situ hybridization of the human Sirtuin 6 gene.
Mahlknecht U
International Journal of Oncology, 28(2), 447-456 (2006)
Minna Rahnasto-Rilla et al.
Chembiochem : a European journal of chemical biology, 17(1), 77-81 (2015-11-27)
Sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) is an NAD+-dependent histone deacetylase enzyme that is involved in multiple molecular pathways related to aging. Initially, it was reported that SIRT6 selectively deacetylated H3K9Ac and H3K56Ac; however, it has more recently been shown to preferentially hydrolyze long-chain
Overexpression of sirtuin 6 suppresses inflammatory responses and bone destruction in mice with collagen-induced arthritis.
Lee HS
Arthritis and Rheumatism, 65(7), 1776-1785 (2013)
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej


![[Tyr(SO3H)63]-Hirudin Fragment 54-65 ≥95% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/401/056/a0ac1972-7f9e-45b9-8e32-74f3f275e097/640/a0ac1972-7f9e-45b9-8e32-74f3f275e097.png)
