Kluczowe dokumenty
SAB4200767
Przeciwciało przeciwko katepsynieD, mysie monoklonalne
clone CTD-19, purified from hybridoma cell culture
Synonim(y):
Anty-CTSD, rozszczepiony na następujące 2 łańcuchy: Łańcuch lekki katepsyny D i łańcuch ciężki katepsyny D
About This Item
Polecane produkty
pochodzenie biologiczne
mouse
Poziom jakości
forma przeciwciała
purified from hybridoma cell culture
rodzaj przeciwciała
primary antibodies
klon
CTD-19, monoclonal
Formularz
buffered aqueous solution
reaktywność gatunkowa
human, rabbit
stężenie
~1.0 mg/mL
metody
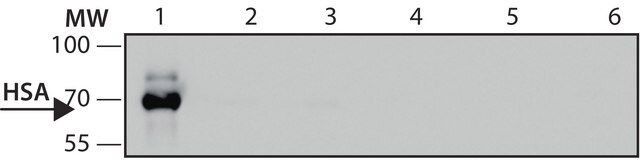
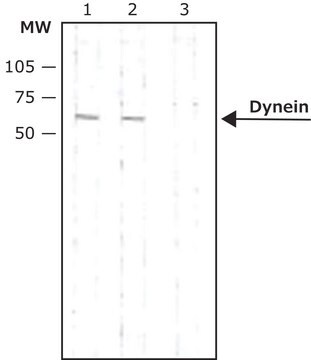
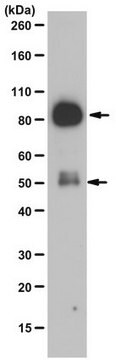
immunoblotting: 2-4 μg/mL using human breast cancer MCF7 cell line
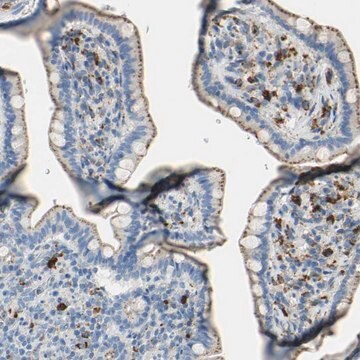
immunofluorescence: 5-10 μg/mL using HeLa cells
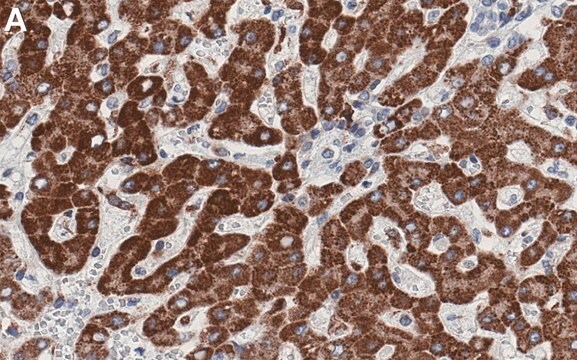
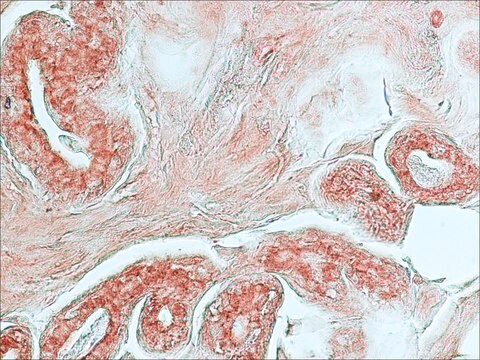
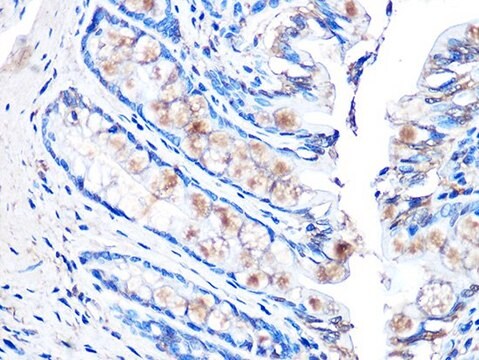
immunohistochemistry: 10-20 μg/mL using heat-retrieved formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human liver sections
izotyp
IgG2a
numer dostępu UniProt
Warunki transportu
dry ice
temp. przechowywania
−20°C
docelowa modyfikacja potranslacyjna
unmodified
informacje o genach
human ... CTSD(1509)
Opis ogólny
Immunogen
Zastosowanie
- immunoblottingu
- immunohistochemia
- immunofluorescencja
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Postać fizyczna
Nie możesz znaleźć właściwego produktu?
Wypróbuj nasz Narzędzie selektora produktów.
Kod klasy składowania
10 - Combustible liquids
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Nie widzisz odpowiedniej wersji?
Jeśli potrzebujesz konkretnej wersji, możesz wyszukać konkretny certyfikat według numeru partii lub serii.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej