Kluczowe dokumenty
R4268
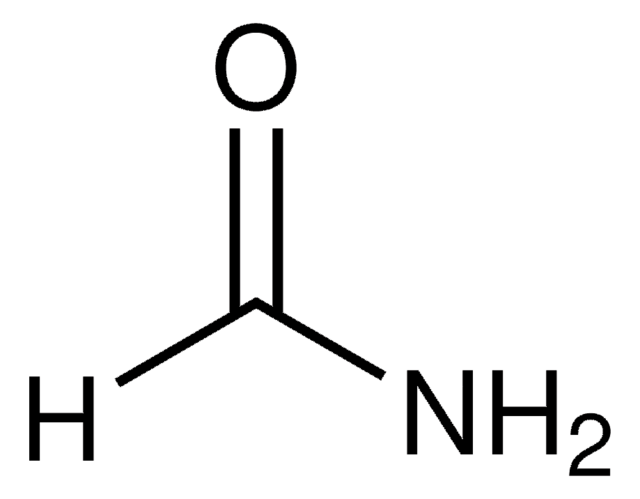
RNA Sample Loading Buffer
for NA electrophoresis, with ethidium bromide (50 μg/mL)
About This Item
Polecane produkty
klasa czystości
for molecular biology
Poziom jakości
Formularz
liquid
stężenie
1.25 ×
metody
electrophoresis: suitable
obecność zanieczyszczeń
RNase, none detected
temp. przechowywania
−20°C
−20°C
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
RNA Sample Loading Buffer has been used as a sample loading buffer in northern blot.
Komponenty
Ilość
produkt powiązany
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Carc. 1B - Muta. 2 - Repr. 1B - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT RE 2 Oral
Organy docelowe
Blood
Kod klasy składowania
6.1C - Combustible, acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wykazy regulacyjne
Wykazy regulacyjne dotyczą głównie produktów chemicznych. Można w nich podawać ograniczoną liczbę informacji na temat produktów niechemicznych. Brak wpisu oznacza, że żaden ze składników nie znajduje się w wykazie. Użytkownik odpowiada za zagwarantowanie bezpiecznego i zgodnego z prawem stosowania produktu.
EU REACH SVHC Candidate List
EU REACH Annex XVII (Restriction List)
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej