Key Documents
M8421
Monoclonal Anti-Myosin (Skeletal, Slow) antibody produced in mouse
clone NOQ7.5.4D, ascites fluid
Synonim(y):
Anti-CMD1S, Anti-CMH1, Anti-MPD1, Anti-MYHCB, Anti-SPMD, Anti-SPMM
About This Item
Polecane produkty
pochodzenie biologiczne
mouse
Poziom jakości
białko sprzężone
unconjugated
forma przeciwciała
ascites fluid
rodzaj przeciwciała
primary antibodies
klon
NOQ7.5.4D, monoclonal
zawiera
15 mM sodium azide
reaktywność gatunkowa
sheep, rat, bovine, hamster, pig, canine, feline, goat, chicken, mouse, rabbit, human, guinea pig
opakowanie
antibody small pack of 25 μL
metody
electron microscopy: suitable
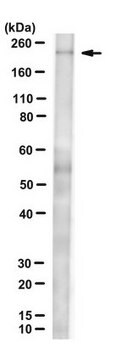
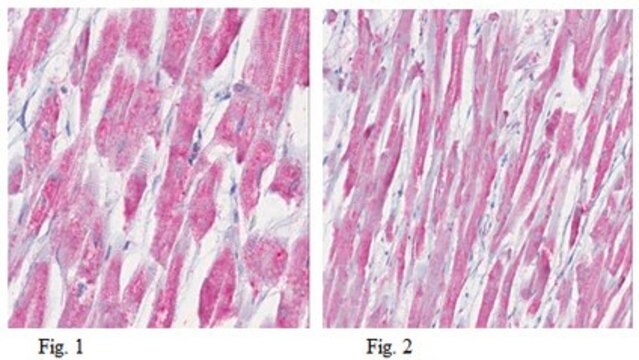
immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections): 1:4,000 using protease-digested, sections of rabbit tongue
indirect ELISA: suitable
radioimmunoassay: suitable
western blot: 1:5,000 using extract of rat or rabbit tongue
izotyp
IgG1
numer dostępu UniProt
Warunki transportu
dry ice
temp. przechowywania
−20°C
docelowa modyfikacja potranslacyjna
unmodified
informacje o genach
human ... MYH7(4625)
mouse ... Myh7(140781)
rat ... Myh7(29557)
Opis ogólny
Monoclonal Anti-Myosin (Skeletal, Slow) (mouse IgG1 isotype) is derived from the NOQ7.5.4D hybridoma produced by the fusion of mouse myeloma cells and splenocytes from BALB/c mice. Myosin, purified from myofibrils isolated from human skeletal muscle, was used as the immunogen.1-3. The isotype is determined by a double diffusion immunoassay using Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Isotyping Reagents, Catalog Number ISO2.
Specyficzność
Immunogen
Zastosowanie
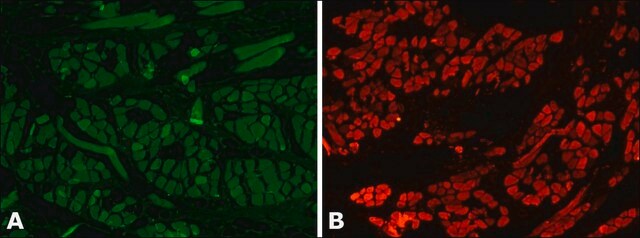
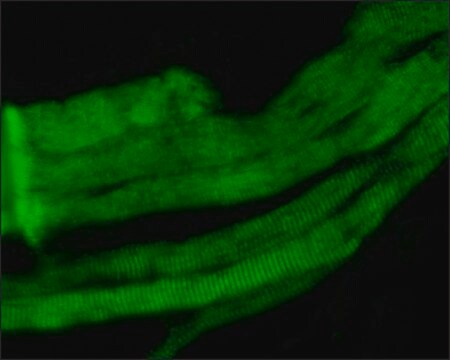
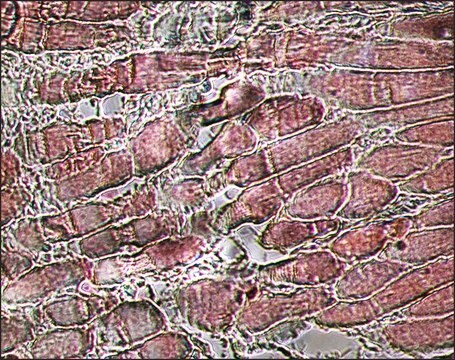
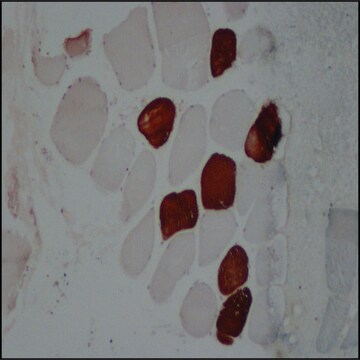
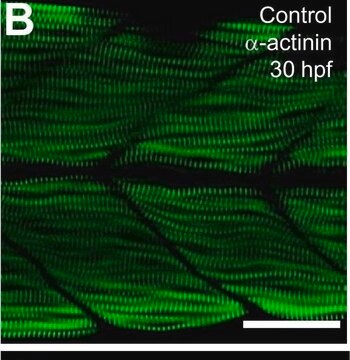
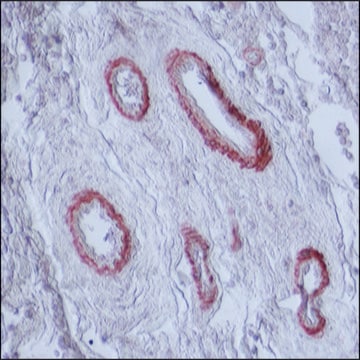
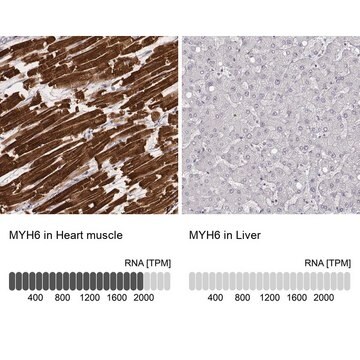
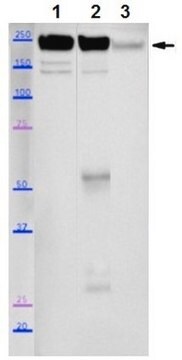
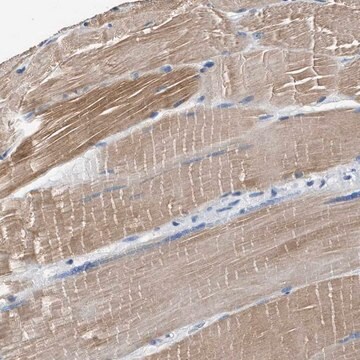
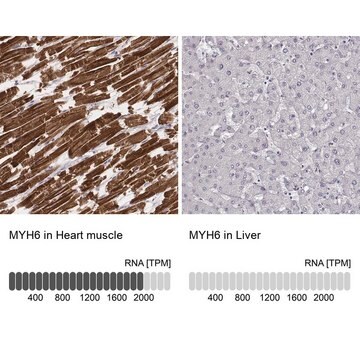
Monoclonal Anti-Myosin (Skeletal, Slow) antibody has been used in the detection of Myosin 7 using:
- light microscopy
- immunofluorescence staining
- immunoblotting
- ELISA
- solid-phase RIA
- immunohistology (frozen, formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded and methacarn-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections)
- immunoelectronmicroscopy
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Transient expression of different myosin isoforms occurs during fetal growth and development. Mutations in myosin 7 is associated with laing distal myopathy (LDM). Myosin 7 gene mutations results in muscular dystrophy diseases like scapuloperoneal myopathy. Mutations leads to storage of myosin protein aggregates in muscle, leading to myosin storage myopathy. Mutations in MYH7 is also associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and in heart malformation disease called ebstein anomaly.
Postać fizyczna
Przechowywanie i stabilność
Oświadczenie o zrzeczeniu się odpowiedzialności
Nie możesz znaleźć właściwego produktu?
Wypróbuj nasz Narzędzie selektora produktów.
Kod klasy składowania
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Poszukaj Certyfikaty analizy (CoA), wpisując numer partii/serii produktów. Numery serii i partii można znaleźć na etykiecie produktu po słowach „seria” lub „partia”.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej