Kluczowe dokumenty
G1424
Globomycin from Streptomyces hagronensis
Synonim(y):
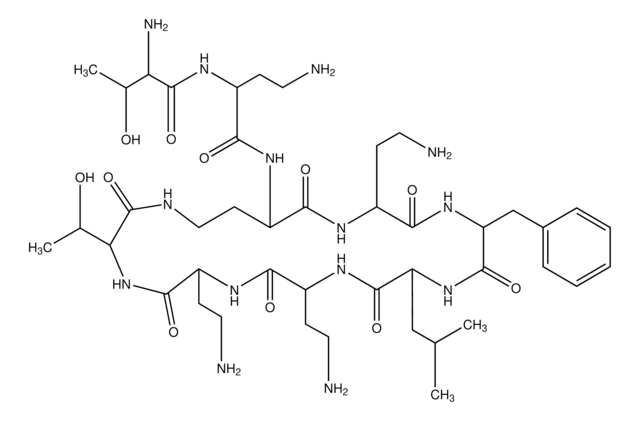
Globomycin, Glycine, N-(N-(N-(N-(N-(3-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-oxononyl)-N-methylleucyl)-L-alloisoleucyl)-L-seryl)-L-allothreonyl)-, rho-lactone, SF 1902
About This Item
Polecane produkty
pochodzenie biologiczne
Streptomyces hagronensis
Poziom jakości
Próba
≥98% (HPLC)
Postać
powder
kolor
white
rozpuszczalność
DMSO: 1 mg/mL
spektrum działania antybiotyku
Gram-negative bacteria
Tryb działania
enzyme | inhibits
temp. przechowywania
−20°C
−20°C
InChI
1S/C32H57N5O9/c1-9-11-12-13-14-24-20(6)32(45)37(8)23(15-18(3)4)29(42)35-26(19(5)10-2)31(44)34-22(17-38)28(41)36-27(21(7)39)30(43)33-16-25(40)46-24/h18-24,26-27,38-39H,9-17H2,1-8H3,(H,33,43)(H,34,44)(H,35,42)(H,36,41)
Klucz InChI
VFGBXFZXJAWPOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
- Globomycin, a new peptide antibiotic with spheroplast-forming activity. I. Taxonomy of producing organisms and fermentation.: This study explores the taxonomy of the producing organisms of Globomycin and details the fermentation processes involved. This antibiotic shows spheroplast-forming activity, indicating its potential application in targeting bacterial cell wall synthesis (Inukai et al., 1978).
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Poszukaj Certyfikaty analizy (CoA), wpisując numer partii/serii produktów. Numery serii i partii można znaleźć na etykiecie produktu po słowach „seria” lub „partia”.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej