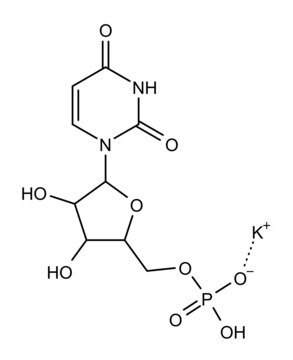
D8515
Deoxyribonucleic acid−cellulose double-stranded from calf thymus DNA
lyophilized powder
Synonim(y):
DNA, Deoxyribonucleic acid, ds-DNA-Cellulose, DNA-Cellulose
Zaloguj sięWyświetlanie cen organizacyjnych i kontraktowych
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Postać
lyophilized powder
zakres etykietowania
3-8 mg double-stranded calf thymus DNA/g
temp. przechowywania
−20°C
Opis ogólny
Deoxyribonucleic acid−cellulose double-stranded from calf thymus DNA, also known as ctDNA is a natural source of DNA designed for DNA binding agent studies. The detection limits of ctDNA are around 2.0ng and the linear ranges of light scattering intensity (I(LS)) is 0.05-1.5 mµg.
Zastosowanie
Deoxyribonucleic acid−cellulose double-stranded from calf thymus DNA is used to study the binding parameters and binding specificity of a variety of proteins, nucleotides, and chemical reagents including anti-cancer agents. It is frequently used in pull-down assays and chromatographic procedures.
Jakość
May contain a trace of Tris and EDTA.
This page may contain text that has been machine translated.
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Poszukaj Certyfikaty analizy (CoA), wpisując numer partii/serii produktów. Numery serii i partii można znaleźć na etykiecie produktu po słowach „seria” lub „partia”.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Yi Zhou et al.
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950), 198(7), 2568-2577 (2017-02-22)
CD74 mediates MHC class-II antigenic peptide loading and presentation and plays an important role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus. C57BL/6
Lutz Wobbe et al.
Nucleic acids research, 41(13), 6553-6567 (2013-05-08)
The molecular function of mTERFs (mitochondrial transcription termination factors) has so far only been described for metazoan members of the protein family and in animals they control mitochondrial replication, transcription and translation. Cells of photosynthetic eukaryotes harbour chloroplasts and mitochondria
S S Zhang et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 266(30), 20483-20490 (1991-10-25)
Two DNA helicases from calf thymus nuclei have been purified and characterized. The two proteins, designated as nuclear DNA helicase I and II, were copurified on Bio-Rex 70, DEAE-Sepharose, phosphocellulose and subsequently separated from each other on a heparin-Sepharose column.
A Georgaki et al.
Nucleic acids research, 22(7), 1128-1134 (1994-04-11)
A DNA helicase from calf thymus, called DNA helicase F, copurified with replication protein A through several steps of purification including DEAE-Sephacel, hydroxyapatite and single stranded DNA cellulose. It is finally separated from replication protein A on FPLC Mono Q
T Kuzuhara et al.
Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 362(4), 805-810 (2007-09-04)
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) inducing protein (Tipalpha) is a carcinogenic factor secreted from Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), mediated through both enhanced expression of TNF-alpha and chemokine genes and activation of nuclear factor-kappaB. Since Tipalpha enters gastric cancer cells, the Tipalpha
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej