Kluczowe dokumenty
C8919
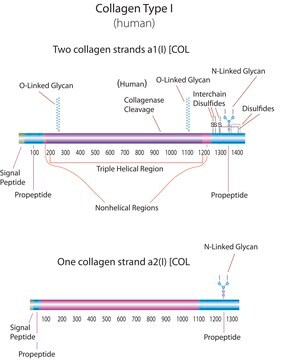
Bovine Collagen Type I
from bovine skin, liquid, 1 mg/mL, suitable for cell culture
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Nazwa produktu
Collagen from calf skin, Bornstein and Traub Type I, (0.1% solution in 0.1 M acetic acid), aseptically processed, BioReagent, suitable for cell culture
pochodzenie biologiczne
bovine (calf) skin
Poziom jakości
sterylność
aseptically processed
linia produktu
BioReagent
Formularz
solution (0.1% solution in 0.1 M acetic acid)
opakowanie
pkg of 20 mL
stężenie
(0.1% solution in 0.1 M acetic acid)
metody
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
pokrycie powierzchni
6‑10 μg/cm2
Specyficzność wiązania
Peptide Source: Collagen
Peptide Source: Elastin
Peptide Source: Fibronectin
Warunki transportu
wet ice
temp. przechowywania
2-8°C
informacje o genach
bovine ... COL1A1(282187) , COL2A1(407142)
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
- for pre-coting glass slides for immunofluorescence studies
- as a cell adhesion factor and modification of poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene) (P(VDF-TrFE)) films for neuron culture
- for coating culture dishes for murine embryonic fibroblasts culture
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Komponenty
Uwaga dotycząca przygotowania
Inne uwagi
Kod klasy składowania
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
nwg
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
Attachment Factors for 3-Dimensional Cell Culture
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is secreted by cells and surrounds them in tissues.
Cancer stem cell media, spheroid plates and cancer stem cell markers to culture and characterize CSC populations.
Extracellular matrix proteins such as laminin, collagen, and fibronectin can be used as cell attachment substrates in cell culture.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej