Kluczowe dokumenty
A1729
Activin B human
≥90% (SDS-PAGE), recombinant, expressed in CHO cells, lyophilized, suitable for cell culture
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Nazwa produktu
Activin B human, recombinant, expressed in CHO cells, suitable for cell culture
pochodzenie biologiczne
human
Poziom jakości
rekombinowane
expressed in CHO cells
Próba
≥90% (SDS-PAGE)
Formularz
lyophilized
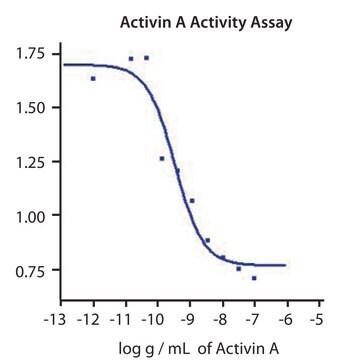
siła działania
0.30-1.50 ng/mL ED50
masa cząsteczkowa
calculated mol wt ~14.5 kDa
opakowanie
pkg of 5 μg
warunki przechowywania
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
metody
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
zanieczyszczenia
endotoxin, tested
temp. przechowywania
−20°C
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Similar to activin-A, activin-B modulates follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) secretion and hemoglobin synthesis, DePaolo LV, et al. (1992); Mason AJ, et al. (1989). It is involved in regulation of the menstrual cycle, Liu J, et al. (2001).
Activin-B is not essential for embryo development or survival, but it does have important roles in development. It stimulates spermatogonial proliferation, Mather JP, et al. (1990) and is localized in specific cells, gonocytes and interstitial Leydig cells, and tissues, rete testis and epididymal epithelium, associated with human testis duct system development, Anderson RA, et al. (2002). Activin-B is found in follicle cells surrounding oocytes, Dohrmann CE, et al. (1993) and been shown to increase the rate of oocytes maturation in a dose and time dependent manner, Pang Y and Ge W. (1999, 2002). It is required for successful mammogenesis leading to lactation, Robinson GW and Hennighausen L. (1997). Recent studies suggest that activin-B may regulate adipocyte differentiation, Kogame, M, et al. (2006).
Activin-B has been linked to several aspects of embryo development. Activin-B is first detected in blastula-stage embryos, Thomsen G, et al. (1990) after midblastula transition and homogeneously distributed during blastula and early gastrula stages. It becomes restricted to the dorso-anterior region in neurula-stage embryos and by early tailbud stage it is restricted to brain, eye anlagen, visceral pouches, otic vesicles and the anterior notochord, Dohrmann CE, et al. (1993). Activin-A and -B localizations are different in 3.5 and 4.5 day mouse blastocyst, Paulusman CC, et al. (1994).
Nakamura, T et al. (1992) suggested that the primary function of Activin-B may involve mesoderm-inducing activity and early development modulation. Schrewe H, et al (1994) and Vassalli A, et al. (1994), reported that activin-B was not essential for survival or for mesoderm formation (in mouse), but that it played a role in late fetal development and female fecundity. A role for activin-B in axial formation was suspected because ectopic expression produced second body axis embryos, Thomsen G, et al. (1990), Mitrani E, et al. (1990).
The roles of activin-B during embryo development are starting to emerge. Activin-B may modulate gap junction permeability in embryos, Olson DJ and Moon RT. (1992). Activin-B has been shown to modulate the morphogenesis of the roof plate (RP) of midbrain wherein it inhibits roof plate differentiation, Alexandre P, et al. (2006). Activin-B signals cell cycle arrest in cells of the involuting dorsal axial mesoderm, Ramis JM, et al. (2007).
Activin-B is involved in the development of the adrenal gland and pancreas. It is present in normal adrenal medulla, but absent in the cortex, Salmenkivi K et al. (2001). Interestingly, Activin-B may be a marker for benign adrenal pheochromocytomas, Salmenkivi K et al. (2001).
The role of activin-B in pancreas development is of particular interest because of efforts to use human embryonic stem cells (hESC) as precursors to make insulin producing cells for treatment of diabetes. Activin-B has been shown to promote expression of the pancreas marker Pdx1 gene in cells of differentiated embryoid bodies (EB), in culture, Frandsen U, et al. (2007). Most recently, Jafary H, et al. (2008) induced insulin-secreting cells for ES by adding activin-B to nestin-positive selection protocol cell.
Postać fizyczna
Komentarz do analizy
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Warning
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Eye Irrit. 2
Kod klasy składowania
3 - Flammable liquids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 2
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej