Key Documents
M0370000
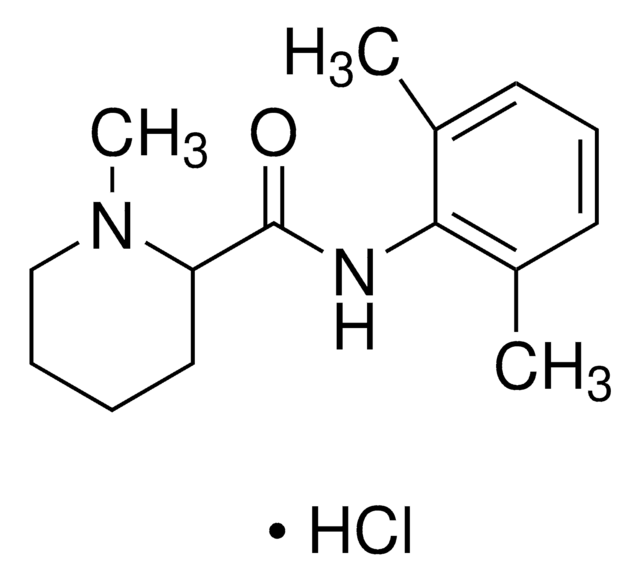
Mepivacaine hydrochloride
European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard
Synonim(y):
1-Methyl-2′,6′-pipecoloxylidine hydrochloride, N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)-1-methyl-2-piperidinecarboxamide hydrochloride
About This Item
Polecane produkty
klasa czystości
pharmaceutical primary standard
rodzina API
mepivacaine
producent / nazwa handlowa
EDQM
Zastosowanie
pharmaceutical (small molecule)
format
neat
temp. przechowywania
2-8°C
ciąg SMILES
CN1CCCCC1C(NC2=C(C)C=CC=C2C)=O.Cl
InChI
1S/C15H22N2O.ClH/c1-11-7-6-8-12(2)14(11)16-15(18)13-9-4-5-10-17(13)3;/h6-8,13H,4-5,9-10H2,1-3H3,(H,16,18);1H
Klucz InChI
RETIMRUQNCDCQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
informacje o genach
human ... SCN10A(6336) , SCN11A(11280) , SCN1A(6323) , SCN2A(6326) , SCN3A(6328) , SCN4A(6329) , SCN5A(6331) , SCN7A(6332) , SCN8A(6334) , SCN9A(6335)
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Powiązane kategorie
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Opakowanie
Inne uwagi
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Acute Tox. 3 Oral - STOT SE 3
Organy docelowe
Central nervous system
Kod klasy składowania
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Przepraszamy, ale COA dla tego produktu nie jest aktualnie dostępny online.
Proszę o kontakt, jeśli potrzebna jest pomoc Obsługa Klienta
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej