Key Documents
69889
MES monohydrate
BioUltra, for molecular biology, ≥99.5% (T)
Synonim(y):
2-Morpholinoethanesulfonic acid hydrate,, 2-morpholin-4-ylethanesulfonic acid;hydrate, 2-(N-Morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid, 4-Morpholineethanesulfonic acid monohydrate
About This Item
Polecane produkty
klasa czystości
for molecular biology
Poziom jakości
linia produktu
BioUltra
Próba
≥99.5% (T)
Postać
powder or crystals
zanieczyszczenia
DNases, none detected
Insoluble matter, passes filter test
Phosphatases, none detected
Proteases, none detected
RNases, none detected
pozostałość po prażeniu (900°C)
≤0.05% (as SO4)
pH
2.5-4.0 (25 °C, 0.5 M in H2O)
przydatny zakres pH
5.5-6.7
pKa (25°C)
6.1
mp
>300 °C (lit.)
rozpuszczalność
H2O: 0.5 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless
gęstość
10.66 g/mL
ślady anionów
chloride (Cl-): ≤50 mg/kg
sulfate (SO42-): ≤50 mg/kg
ślady kationów
Al: ≤5 mg/kg
As: ≤0.1 mg/kg
Ba: ≤5 mg/kg
Bi: ≤5 mg/kg
Ca: ≤20 mg/kg
Cd: ≤5 mg/kg
Co: ≤5 mg/kg
Cr: ≤5 mg/kg
Cu: ≤5 mg/kg
Fe: ≤5 mg/kg
K: ≤50 mg/kg
Li: ≤5 mg/kg
Mg: ≤5 mg/kg
Mn: ≤5 mg/kg
Mo: ≤5 mg/kg
Na: ≤50 mg/kg
Ni: ≤5 mg/kg
Pb: ≤5 mg/kg
Sr: ≤5 mg/kg
Zn: ≤5 mg/kg
λ
0.5 M in H2O
absorpcja UV
λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.025
λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.020
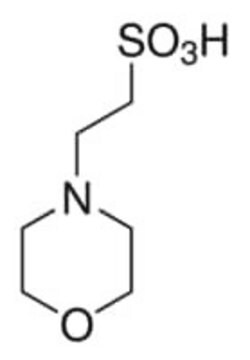
ciąg SMILES
O.OS(=O)(=O)CCN1CCOCC1
przydatność
suitable for DNase I test
suitable for Western blot
suitable for molecular biology
Zastosowanie
clinical research
diagnostic assay manufacturing
life science and biopharma
obecność zanieczyszczeń
DNase, none detected
NICKase, none detected
RNase, none detected
protease, none detected
InChI
1S/C6H13NO4S.H2O/c8-12(9,10)6-3-7-1-4-11-5-2-7;/h1-6H2,(H,8,9,10);1H2
Klucz InChI
MIIIXQJBDGSIKL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
- In the preparation of a solution used for the suspension and dilution of protoplasts to measure the density and number of protoplasts using a haemocytometer
- As a component of Murashige and Skoog basal salt media
- In the preparation of total ionic strength adjustment buffer (TISAB)
- as a constituent in mobile phase solutions employed for the analysis of high molecular weight species and charge-related variants of biopharmaceutical proteins through SEC, HIC, and IEX chromatographic techniques
Cechy i korzyści
- Suitable as a Buffer component, for Electrophoresis and Molecular Biology
- Effective Buffering from pH 2.5-4.0 (25 °C, 0.5 M in H2O) with a pKa of 6.1 (25 °C)
- Free from DNase, NICKase, RNase, and Protease
Uwaga dotycząca przygotowania
Inne uwagi
Sterilization: Sterilization should be by filteration through 0.2 uM filters. Autoclaving is not recommended by any sulfonic acid buffers. If buffers must be nuclease-free, it is best to treat the water, and then add the buffer solids after autoclaving. When MES solutions are autoclaved, they turn yellow (although pH does not change measurably. The identity of the yellow breakdown product is unknown.
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 1
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej